Continental tug-of-war – until the rope snaps
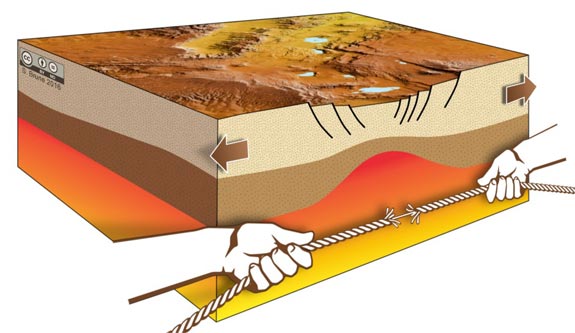
The extension velocity of tectonic plates increases rapidly during continental separation. The reason is that plate speed is dependent on the strength of the rift zone, which decreases abruptly during continental stretching – similar to a rupturing rope. (Fig: GFZ, S.Brune , G. Schwalbe , S. Riedl)
Present-day continents were shaped hundreds of millions of years ago as the supercontinent Pangaea broke apart. Derived from Pangaea’s main fragments Gondwana and Laurasia, the current continents move at speeds of 20 to 80 millimeters per year characterizing today’s plate tectonics.
Continental breakup is still not completely scientifically understood. New research, published in the scientific journal “Nature” shows that the continents initially stretch very slowly along the future splitting zone, but then move apart very quickly before the onset of rupture. The final speed can be up to 20 times faster than in the first, slow extension phase.
Of course these processes have to be seen from the geological perspective: we are talking about plates moving slowly over long time periods, centimeters per year and millions of years, respectively. South America for instance separated from Africa over a period of approximately 40 million years.
The separation process, called 'rifting' by geoscientists, began about 150 million years ago, while the two tectonic plates diverged only with 5 to 7 millimeters per year. This slowly thinned the earth's crust and led to the formation of a basin. Before the two continents separated, however, the rift velocity increased six-fold to around 40 millimeters per year. Today Africa and South America drift apart annually with about 35 millimeters per year.
“Imagine the rope snapping during a tug-of-war” describes Sascha Brune from the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences, lead author of the study. “At first the rope strains slowly and imperceptibly, when one fiber breaks the overall strength of the rope doesn’t change much; but rupture of the last few rope fibers occurs very abruptly.”
Together with colleagues from the University of Sydney the scientist has investigated numerous different rift zones worldwide and found that many continental breakups proceeded according to this two-phase speed evolution: “Most dramatic was the case of the separation of North America and Africa,” says Brune. “Roughly 240 million years ago, divergence began very slowly with only one millimeter per year.” 200 million years ago, however rifting accelerated by 20 times.
Intriguingly, rift acceleration typically began about ten million years before the actual rupture of the continent, as seen during the separation of Australia and Antarctica, North America and Greenland, Africa and South America, in the North Atlantic or the South China Sea.
Therefore, the newly formed continental margins are significantly shaped by both speed stages: first, slow rifting formed the shelf regions that today are located not far below sea level and near to the coast. In the second phase the distal, deep-water domains of the continental margin were formed at higher rift velocity inducing enhanced faulting and greater volcanic activity.
The new geoscientific results have important implications for the theory of plate tectonics: today's movements of the tectonic plates are known to be governed by the descent and collision of plates and by the currents of Earth’s deep mantle. During the breakup of continents, however, rapid plate accelerations are controlled by the weakening of the continent itself and not primarily by processes in the deep interior of the Earth.
Sascha Brune, Simon E. Williams, Nathaniel P. Butterworth, and R. Dietmar Müller: ”Abrupt plate accelerations shape rifted continental margins”, Nature AOP, 18.07.2016, DOI 10.1038/nature18319
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.gfz-potsdam.de/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















