ClpX-ClpP protein complex could be starting point for new antibiotics: Weak spot in pathogenic bacteria
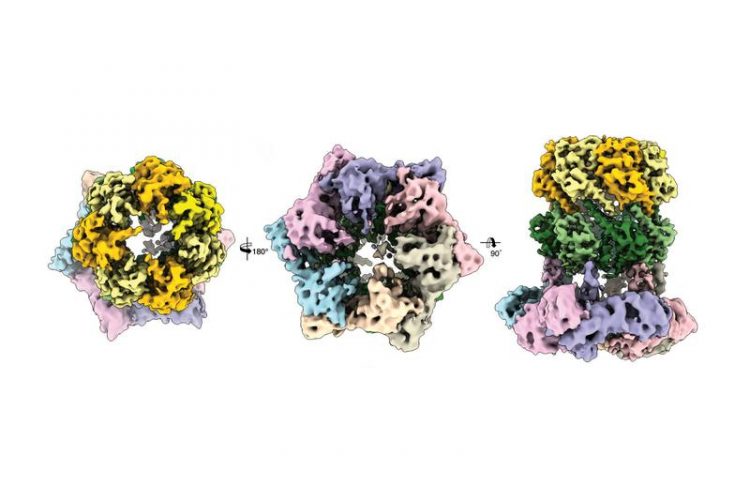
Three cryo-electron microscopic views of the protein complex ClpX-ClpP. Image: C. Gatsogiannis / MPI of Molecular Physiology
Almost 700,000 people in Europe suffer from infections every year through antibiotic-resistant pathogens; approximately 33,000 of them die. Despite this enormous and globally increasing danger, very few new antibiotics have been developed and approved in the past few decades.
There is no improvement in sight. That is why it is urgently necessary to find new points of attack in pathogenic bacteria and to develop new antibiotics which exploit these weak spots.
New mechanism of action destroys bacteria
A particularly promising point of attack for antibacterial therapies is the proteolytic enzyme ClpP: on the one hand it plays an important role in bacterial metabolism, and on the other hand it ensures the controlled degradation of defective proteins.
But for this purpose it requires the ClpX protein as a starting aid. In the complex with ClpP, ClpX identifies proteins which should be degraded, unfurls them and guides them into its barrel-like degradation chamber.
Scientists in the groups led by Prof. Stephan Sieber, Technical University of Munich (TUM) and Prof. Stefan Raunser, Director at the Max Planck Institute of Molecular Physiology in Dortmund, have now elucidated the three-dimensional structure of the ClpX-ClpP proteolytic complex for the first time and thereby established an important basis for future pharmacological strategies.
A new class of potential antibiotics – the so-called acyldepsipeptide (ADEP) antibiotics – also brings about an uncontrolled degradation through ClpP without the support of ClpX. As a result also vital proteins are destroyed – with lethal consequences for the bacteria.
This unique mechanism of action has considerable innovation potential in the fight against pathogenic bacteria. Whereas common antibiotics act through the inhibition of vital processes, in this case the antibacterial effect is achieved through the activation of a process.
Disarming bacteria
In addition to the degradation of defective proteins, ClpP is also a decisive regulator in the production of an arsenal of bacterial toxins which are primarily responsible for the pathogenic effect of many pathogens.
At the TUM, the group led by Prof. Stephan Sieber has been successfully researching the ClpP protease for years, and has already developed a large number of potent inhibitors against ClpP and ClpX which stop the production of bacterial toxins and can therefore more or less disarm them. Dóra Balogh has now managed to produce and stabilize the ClpX-ClpP complex.
New possibilities through the elucidation of the structure of ClpX-ClpP
But up to recently the structure of the ClpX-ClpP complex could not yet be elucidated in detail. Dr. Christos Gatsogiannis, researcher in the group led by Prof. Stefan Raunser at the MPI of Molecular Physiology, has now managed this by means of cryogenic electron microscopy.
With this technology they were able to demonstrate that ADEP and ClpX dock onto ClpP at the same spot, but control the process of protein degradation in a different way: Whereas ClpX does not lead to an alteration in the structure of ClpP, ADEP brings about an unintended opening of the complex. As a result, intact proteins are also degraded in an uncontrolled manner and without the support of ClpX.
The clarification of this mechanism by the research teams from Dortmund and Munich is a milestone on the way to the development of innovative antibiotic substances targeting ClpP.
Further information:
The research work has been sponsored with funds from the European Research Council (ERC), the Max Planck Society and the German Research Foundation (DFG) within the scope of the Collaborative Research Center 1035 (SFB 1035) and the Cluster of Excellence – Center for Integrated Protein Science Munich (CIPSM).
Prof. Dr. Stephan A. Sieber
Technical University of Munich
Chair of Organic Chemistry II
Lichtenbergstr. 4, 85748 Garching, Germany
Tel.: +49 89 289 13302 – E-mail: stephan.sieber@tum.de
Web: https://www.department.ch.tum.de/oc2/home/
Prof. Dr. Stefan Raunser
Max Planck Institut of Molecular Physiology
Structural Biochemistry
Otto-Hanhn-Str. 11, 44227 Dortmund
Tel.: +49 231 133 2300 – E-mail: raunser@mpi-dortmund.mpg.de
Web: https://www.mpi-dortmund.mpg.de/research-groups/raunser/group-members
Cryo-EM structure of the ClpXP protein degradation machinery
C. Gatsogiannis, D. Balogh, F. Merino, S. A. Sieber, S. Raunser
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology, vol. 26, 946–954 (2019)
DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0304-0
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41594-019-0304-0
https://www.tum.de/nc/en/about-tum/news/press-releases/details/35720/ Link to the press release
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















