Researchers find better way to 'herd' electrons in solar fuel devices
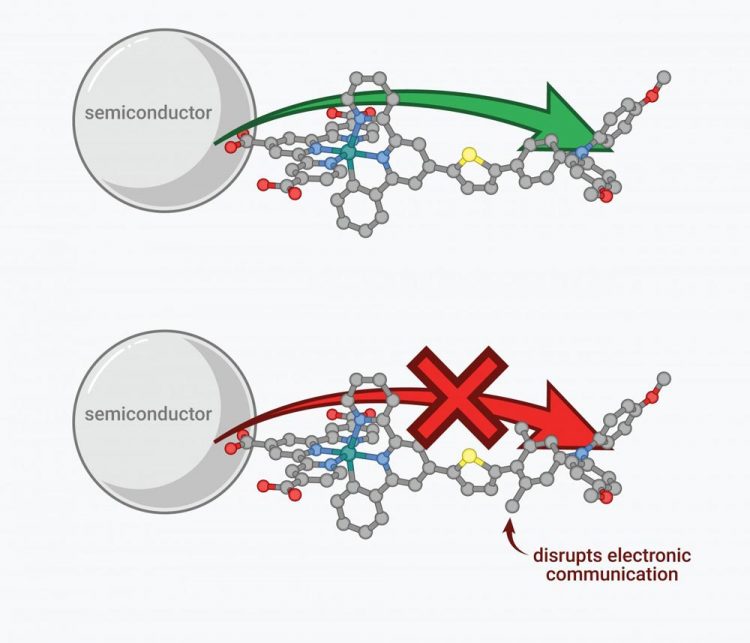
Molecules can be designed to act as a gate and keep electrons moving forward in one direction. Credit: UBC Chemistry
The finding, published today in Nature Chemistry, could have a big impact on devices that convert sunlight into electricity and fuel.
Researchers have already shown that the efficiency of electron transfer at semi-conductor interfaces depends on the distance the electron has to travel. The new finding shows that the efficiency of the transfer also depends on the type of chemical bonds–or the bridge–that the electron travels through along the way.
“Now we can design molecules to act as a gate and keep electrons moving forward in one direction and not reverse their direction,” says UBC chemist and chemical engineer Curtis Berlinguette, senior author on the paper.
“If electrons go in the wrong direction, we lose much of the sun's energy as heat before it can be converted into electricity or fuel.”
The research also has ramifications in how we view electron transfer in biological systems.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















