New microfluidic device tackles tough synthesis tasks
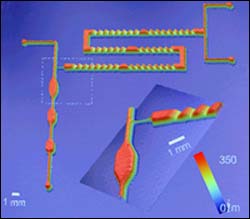
NIST microfluidic device for synthesizing and analyzing polymers and other complex liquids.
A new type of microfluidic device that can help industry to optimize paints, coatings for microelectronics and specialty polymers has been developed by National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) researchers. The device is made of a chemically durable plastic that is resistant to many common organic solvents. It was fabricated with a rapid prototyping method also developed at the agency.
Described in the Aug. 18 issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society,* such devices can be used to make specialty polymers in small amounts, or to rapidly change polymer ingredients so that the impact of expensive additives on material behavior can be systematically analyzed. This is becoming important as more specialty polymers use designer elements for applications in nanotechnology and biotechnology.
Devices typically measure about half the size of a credit card and are made with a technique called “frontal photopolymerization.” The NIST researchers adapted the technique to fabricating microfluidic devices. Ultraviolet light was shined through patterned “stencils” into a liquid layer of a chemical called thiolene. Areas exposed to the light harden into a solid polymer while unexposed areas remain liquid and can be flushed away, leaving relatively deep channels capable of handling thicker fluids than current lab-on-a-chip devices.
In a separate paper,** the NIST researchers provide detailed data about how varying doses of ultraviolet light affect the height of the polymer structures formed. Such data should be helpful for increasing the complexity of devices that can be fabricated with the technique.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Process Engineering
This special field revolves around processes for modifying material properties (milling, cooling), composition (filtration, distillation) and type (oxidation, hydration).
Valuable information is available on a broad range of technologies including material separation, laser processes, measuring techniques and robot engineering in addition to testing methods and coating and materials analysis processes.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















