Using a novel scaffold to repair spinal cord injury
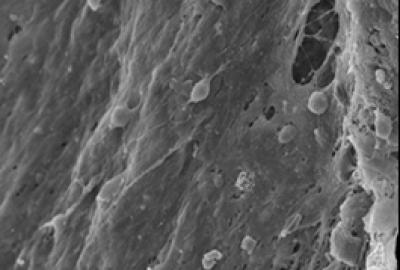
Through transmission electron microscope, neural stem cells attached to the double-layer collagen membrane with unequal pore sizes and there was no structural change in the double-layer collagen membrane. Credit: Neural Regeneration Research
The loose layer was infiltrated with a large amount of neural stem cells before it was transplanted in vivo. Thus a plenty of neural stem cells can be provided at the target spinal cord site.
The loose layer was adhered to the injured side and the compact layer was placed against the lateral side. The compact layer has very small holes, so it can prevent ingrowth of adjacent scar tissue.
It can also prevent the loss of inner neural stem cells and the neural growth factors secreted by the differentiated neural stem cells.
Thus a good microenvironment forms to help spinal cord injury repair. Yuan Ning and colleagues found that transplantation of neural stem cells in a double-layer collagen membrane with unequal pore sizes is an effective therapeutic strategy to repair an injured spinal cord in rats.
Related results were published in Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 10, 2014).
Article: ” Neural stem cell transplantation in a double-layer collagen membrane with unequal pore sizes for spinal cord injury repair,” by Ning Yuan1, Wei Tian1, Lei Sun2, Runying Yuan2, Jianfeng Tao2, Dafu Chen2 (1 Department of Spine, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing, China; 2 Beijing Institute of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Beijing, China) Yuan N, Tian W, Sun L, Yuan RY, Tao JF, Chen DF. Neural stem cell transplantation in a double-layer collagen membrane with unequal pore sizes for spinal cord injury repair. Neural Regen Res. 2014;9(10):1014-1019.
Contact: Meng Zhao
eic@nrren.org
86-138-049-98773
Neural Regeneration Research
http://www.nrronline.org/
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















