Another piece of the ion pump puzzle
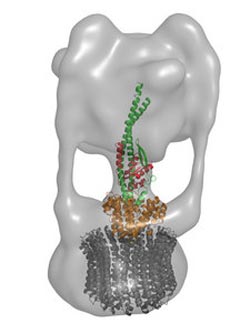
Figure 1: The D (green) and F (red) subunits of the enzyme V-ATPase form a central axis that connects the components of the catalytic V1 segment (upper) and the membrane-bound V0 segment (lower; orange and grey). Copyright : 2012 Takeshi Murata<br>
From bacteria to humans, all cells use molecules of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) as fuel to power a broad range of biochemical reactions. For example, massive multi-subunit enzymes known as V-ATPases convert ATP molecules into energy that helps drive the transport of ions across cellular membranes.
V-ATPases consist of a so-called ‘V1 complex’, which transfers energy derived from ATP hydrolysis into rotational motion, thereby promoting ion transport through to the membrane-bound V0 complex. These two complexes are joined by three ‘stalks’, including a central stalk composed of subunits named D and F, although this segment of the protein is poorly characterized. “The structure of this central axis of V-ATPase has not been obtained,” says Takeshi Murata of the RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center in Yokohama, “and we believe such structural studies are very important to understand this protein’s precise mechanism.”
Murata and colleagues recently succeeded in obtaining high-resolution structural information about the DF complex of V-ATPase obtained from the bacteria Enterococcus hirae1. By comparing this structural information against an equivalent segment from F-ATPase, which synthesizes rather than hydrolyzes ATP, the researchers were able to identify functional domains that may be specifically required by V-ATPases.
They determined that the E. hirae D subunit is composed of a pair of long helical structures coiled around each other, with a short hairpin-shaped loop at one end. According to Murata, the discovery of this latter structure was unexpected. “This short beta-hairpin region is a unique structure, although the rest of the D structure is very similar to that of other rotary complexes such as F-ATPase and flagellar motors,” he says. This segment does not appear to be essential for V-ATPase assembly, but ATP processing efficiency was reduced when the researchers deleted this hairpin from the subunits.
In contrast, the E. hirae F subunit assumed a more compact structure, relatively similar to its A- and F-ATPase counterparts; the researchers determined that it specifically associates with the middle portion of the D subunit’s coiled helical segment, an interaction that depends heavily on a particular helix within the F subunit.
Although untangling this structure represents a major step forward, this complex must also be understood as part of a far larger entity (Fig. 1). Murata and colleagues have already begun tackling this. “We recently succeeded at solving the structure of V1-ATPase with a resolution of 2.1 Angstroms,” says Murata, “and we are now preparing this manuscript for publication.”
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the RIKEN Systems and Structural Biology Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Webb captures top of iconic horsehead nebula in unprecedented detail
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has captured the sharpest infrared images to date of a zoomed-in portion of one of the most distinctive objects in our skies, the Horsehead Nebula….

Cost-effective, high-capacity, and cyclable lithium-ion battery cathodes
Charge-recharge cycling of lithium-superrich iron oxide, a cost-effective and high-capacity cathode for new-generation lithium-ion batteries, can be greatly improved by doping with readily available mineral elements. The energy capacity and…

Novel genetic plant regeneration approach
…without the application of phytohormones. Researchers develop a novel plant regeneration approach by modulating the expression of genes that control plant cell differentiation. For ages now, plants have been the…





















