Flavins keep a handy helper in their pocket
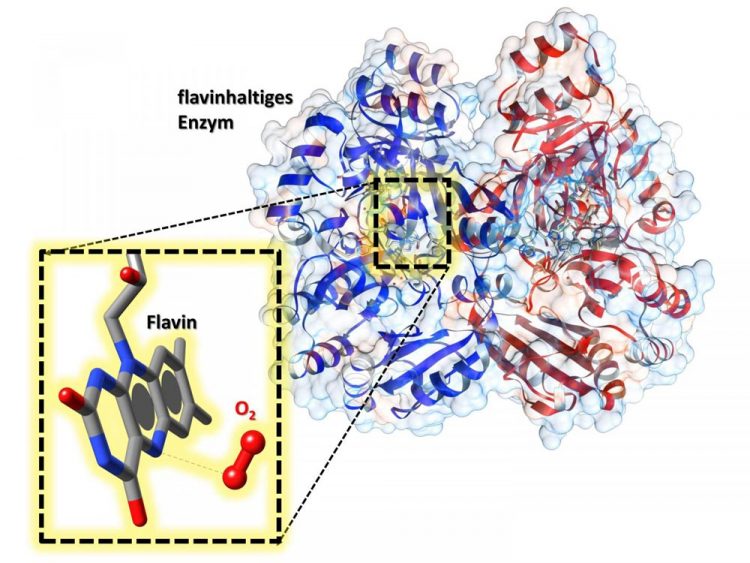
In the active center of the enzyme is a flavin cofactor. In the enlargement we can see that near it, oxygen (O2) is bound -- enabling the flavin to be activated. Source: Robin Teufel, Raspudin Saleem-Batcha
A team headed by Dr. Robin Teufel and Dr. Raspudin Saleem-Batcha of the University of Freiburg at the Center for Biological Systems Analysis has now shown in detail how oxygen interacts with the flavin in an enzyme – revealing for the first time precisely how it works.
The researchers have published their results in the latest Proceedings of the National Academy USA (PNAS).
Flavins play a key role in metabolic processes, in the immune system and in neural development in humans – and are equally important to bacteria, fungi and plants.
Flavoenzymes often require oxygen to function. But until now many of the details of their interaction were not known.
The researchers used x-ray diffraction analysis to show for the first time that oxygen is bound to a special pocket inside the enzyme.
The nature of this compound makes it possible to activate the cofactor – making it essential for the enzyme to work. This knowledge may help, for example, to rationally modify flavoenzymes in the future – in basic research or for biotechnological applications.
###
Original publication:
Raspudin Saleem-Batcha, Frederick Stull, Jacob N. Sanders, Bradley S. Moore, Bruce A. Palfey, K. N. Houk, Robin Teufel: Enzymatic control of dioxygen binding and functionalization of the Flavin cofactor. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA. DOI: 10.1073
http://www.
Contact:
Center for Biological Systems Analysis
University of Freiburg
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















