Breakthrough in hydrogen fuel cells

A team of USC scientists has developed a robust, efficient method of using hydrogen as a fuel source.
Hydrogen makes a great fuel because of it can easily be converted to electricity in a fuel cell and because it is carbon free. The downside of hydrogen is that, because it is a gas, it can only be stored in high pressure or cryogenic tanks.
In a vehicle with a tank full of hydrogen, “if you got into a wreck, you'd have a problem,” said Travis Williams, assistant professor of chemistry at the USC Dornsife College.
A possible solution is to store hydrogen in a safe chemical form. Earlier this year, Williams and his team figured out a way to release hydrogen from an innocuous chemical material — a nitrogen-boron complex, ammonia borane — that can be stored as a stable solid.
Now the team has developed a catalyst system that releases enough hydrogen from its storage in ammonia borane to make it usable as a fuel source. Moreover, the system is air-stable and re-usable, unlike other systems for hydrogen storage on boron and metal hydrides.
The research was published this month in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“Ours is the first game in town for reusable, air stabile ammonia borane dehydrogenation,” Williams said, adding that the USC Stevens Institute is in the process of patenting the system.
The system is sufficiently lightweight and efficient to have potential fuel applications ranging from motor-driven cycles to small aircraft, he said.
The research was funded by the Hydrocarbon Research Foundation and the National Science Foundation.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.usc.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
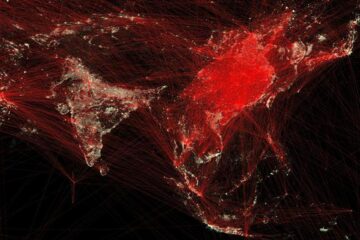
Economies take off with new airports
A global study by an SUTD researcher in collaboration with scientists from Japan explores the economic benefits of airport investment in emerging economies using nighttime satellite imagery. Be it for…
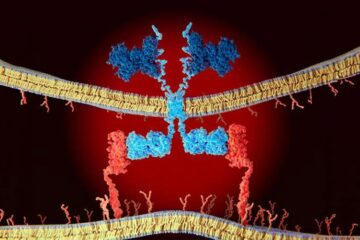
CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets
Pan-cancer analysis uncovers a new class of promising CAR T–cell immunotherapy targets. Scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital found 156 potential CAR targets across the brain and solid tumors,…

Stony coral tissue loss disease
… is shifting the ecological balance of Caribbean reefs. The outbreak of a deadly disease called stony coral tissue loss disease is destroying susceptible species of coral in the Caribbean…





















