Computers determine when to stop searches at sea

The Search and Rescue Survival Model is being developed by the University of Portsmouth’s Sports Science and Mathematics departments and the US Coast Guard.
It aims to support the US Coast Guard target of saving 93 per cent of victims annually – between 3000-6000 people – whose lives are in danger at sea.
“Using this new computer model will take pressure off humans making very emotional and sensitive decisions about when to end a search,” said Professor Mike Tipton, human and applied physiologist, from the University of Portsmouth.
“When the model predicts that a victim can no longer survive, the search and rescue team can stop or redeploy the search.
“It will ensure that Coast Guard personnel are not exposed to the high risks associated with search and rescue operations any longer than necessary and will also help to save time and resources,” he said.
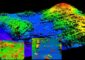
The US Coast Guard currently uses a software system known as SAROPS (Search and Rescue Optimal Planning System) to calculate how far a person will have drifted and how large the search area should be.
Data such as wind speed, sea state and water temperature is entered into SAROPS along with information about the victim’s sex, height, weight and what they were wearing to determine exactly how the search should be conducted.
“Calculating survival time will add another layer to SAROPS; it will be able to predict not only where a search should be conducted but when it should be stopped,” said Professor Tipton.
Chris Turner, Ocean Engineer and Manager for the project for the US Coast Guard in Groton, Connecticut, sought the help of the university because of its international reputation for expertise in the area of survival in the sea.
“The University of Portsmouth has been able to tap into and analyze data held by the Institute of Naval Medicine and the Royal National Lifeboats Institution, both critical to the development of this survival model. To our knowledge no other similar repository of this information exists – even in the US.
“The development of this technology is very exciting. It will be trialled in American waters in late 2009 and once thoroughly tested, the aim is to roll it out to the whole of the US,” he said.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…