New Super H-mode regime could greatly increase fusion power
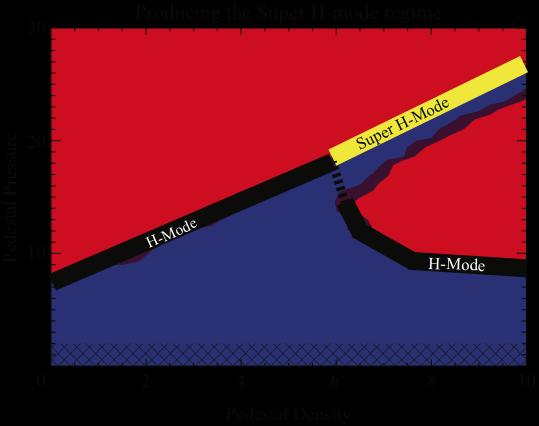
In this figure, the red signifies instability while blue is the quiescent region. Plasma density needs to increase along the narrow blue channel to reach the Super H-mode state. Image adapted from General Atomics
Meet “Super H mode,” a newly discovered state of tokamak plasma that could sharply boost the performance of future fusion reactors. This new state raises the pressure at the edge of the plasma beyond what previously had been thought possible, creating the potential to increase the power production of the superhot core of the plasma.
Discovery of this mode has led to a new line of research within plasma physics that aims to define a path to higher power. The route could prove particularly promising for ITER, the international experiment under construction in France to demonstrate the feasibility of fusion energy.
Researchers led by Wayne Solomon of the U.S. Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) accessed the new state on the DIII-D National Fusion Facility that General Atomics operates for DOE in San Diego. Motivating their findings were theoretical predictions of a plasma state beyond H-mode, the current regime for high-level plasma performance.
Philip Snyder, director of Theory and Computational Science for General Atomics' Energy and Advanced Concepts Group, developed the predictions. His surprising discovery was that a model called EPED predicted more than one type of edge region in tokamak plasmas, with the previously unknown Super H-mode among them.
Such regions are called “pedestals” because they serve as ledges in H-mode plasmas from which the pressure drops off sharply. The higher and wider the pedestal the greater the density and pressure, which together act like thermoses to contain the man-made plasma at more than 100 million degrees C. “It's an important way that we can reach fusion conditions efficiently,” said Snyder, whose model predicted a new pedestal height that corresponds to the super H-mode.
Verification of this prediction is what the researchers found. Their experiments reached the higher Super H-mode regime by steadily increasing density in a quiescent state that naturally avoids pedestal collapses. The results caused the plasma to follow a narrow path to the Super H-mode, the physics equivalent of steering a boat through rocky shores.
###
Contact: Wayne Solomon, (858)-455-3547, wsolomon@pppl.gov
Abstracts: TP12.00090 The EPED Pedestal Model: Validation, Super H-Mode, and Core-Pedestal Coupling
Session Session TP12: Poster Session VII (ICF, Mathematical and Simulation Methods, Basic Theory, DIII-D II, Boundary and Plasma-Material Interactions)
9:30 AM-9:30 AM, Thursday, November 19, 2015
Room: Exhibit Hall A
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















