Multi-species genome comparison sheds new light on evolutionary processes, cancer mutations

NHGRI researchers contribute dog data to groundbreaking study
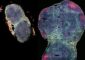
An international team that includes researchers from the National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), part of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), has discovered that mammalian chromosomes have evolved by breaking at specific sites rather than randomly as long thought – and that many of the breakage hotspots are also involved in human cancer.
In a study published in the July 22 issue of the journal Science, a team of 25 scientists from the United States, France and Singapore compared the organization of the chromosomes of eight mammalian species: human, mouse, rat, cow, pig, dog, cat and horse. Using sophisticated computer software to align and compare the mammals’ genetic material, or genomes, the team determined that chromosomes tend to break in the same places as species evolve, resulting in rearrangements of their DNA. Prior to the discovery of these breakage hotspots, the prevailing view among scientists was that such rearrangements occurred at random locations.
“This study shows the tremendous power of using multi-species genome comparisons to understand evolutionary processes, including those with potential relevance to human disease,” said NHGRI Scientific Director Eric D. Green, M.D., Ph.D. “The dog genome map generated by NHGRI researchers and their collaborators played a key role in these new analyses. Furthermore, the team took full advantage of the wealth of human, mouse and rat genome sequence data generated by the recently completed Human Genome Project.”
Chromosomes are the threadlike “packages” of DNA located in the nucleus of each cell. When cells divide, a chromosome occasionally breaks and the fragment can get stuck onto another chromosome. In addition, fragments may break off from two different chromosomes and swap places.
Chromosomal breakages, also referred to as translocations, are thought to be important in terms of evolution. When chromosomes break in egg or sperm cells, opportunities arise for the rearrangement of DNA in the resulting offspring. Such inheritable rearrangements may be lethal or cause disease. However, in some cases, the breaks may lead to the production of new or altered proteins with potential to benefit an organism. In addition to their evolutionary implications, chromosomal translocations are known to contribute to the development or progression of many types of cancer.
In their paper, researchers report that the chromosomal abnormalities most frequently associated with human cancer are far more likely to occur in or near the evolutionary breakage hotspots than are less common types of cancer-associated abnormalities. Researchers theorize that the rearrangements seen near breakage hotspots may activate genes that trigger cancer and/or inactivate genes that normally suppress cancer. However, they emphasize that far more work remains to be done to clarify the relationship between cancer and the breakage hotspots. One thing researchers have determined is that the regions immediately flanking the breakage hotspots contain more genes, on average, than the rest of the genome.
The team was led by Harris A. Lewin, Ph.D., of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and William J. Murphy, Ph.D., of Texas A&M University in College Station. Mapping data for the dog genome were provided by NHGRI’s Elaine Ostrander, Ph.D., and Heidi G. Parker, Ph.D., along with scientists from the French National Center for Scientific Research at the University of Rennes. Other study participants were from the National Cancer Institute, the Genome Institute of Singapore and the University of California at San Diego.
“Science tells us that the most effective tool we currently have to understand our own genome is to compare it with the genomes of other organisms. With each new genome that we sequence, we move closer to filling the gaps in our knowledge,” said Dr. Ostrander, who is chief of the Cancer Genetics Branch in NHGRI’s Division of Intramural Research.
The multi-species comparison published in Science also yielded surprising results about the rate at which chromosomal evolution occurs. Based on an analysis that included a computer-generated reconstruction of the genomes of long-extinct mammals, researchers found the rate of chromosomal evolution among mammals dramatically accelerated following the extinction of the dinosaurs about 65 million years ago.
Before the sudden demise of dinosaurs and many other types of animals, which is thought to have resulted from a massive comet or asteroid striking Earth, mammals shared fairly similar body plans and also fairly similar genomes. Researchers speculate that the mass extinction opened new ecological niches for mammals, spurring their diversification and the emergence of new mammalian orders. This situation would have facilitated opportunities for the isolation of mammals into more distinct breeding groups, speeding the development of species-specific chromosomes.
“This study has revealed many hidden secrets on the nature and timing of genome evolution in mammals, and it demonstrates how the study of basic evolutionary processes can lead to new insights into the origin of human diseases,” said Dr. Lewin, who is director of the Institute of Genomic Biology at the University of Illinois.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nih.govAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
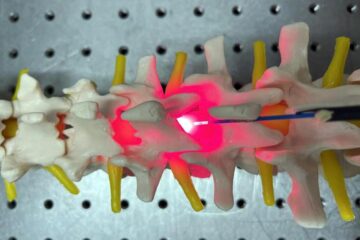
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….