Giant channels discovered beneath Antarctic ice shelf
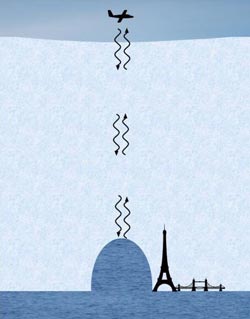
This is a schematic diagram indicating the approximate scale of one of the ice shelf channels, similar in height to the Eiffel Tower, and Tower Bridge in width.<br><br>Credit: Anne Le Brocq<br>
Scientists have discovered huge ice channels beneath a floating ice shelf in Antarctica. At 250 metres high, the channels are almost as tall as the Eiffel tower and stretch hundreds of kilometres along the ice shelf.
The channels are likely to influence the stability of the ice shelf and their discovery will help researchers understand how the ice will respond to changing environmental conditions.
Researchers from the University of Exeter, Newcastle University, the University of Bristol, the University of Edinburgh, the British Antarctic Survey and the University of York, used satellite images and airborne radar measurements to reveal the channels under the ice shelf. The channels can be seen on the surface of the ice shelf, as well as underneath, because the ice floats at a different height depending on its thickness.
The researchers also predicted the path of meltwater flowing under the part of the ice in contact with the land – known as the ice sheet. They discovered that the predicted flow paths lined up with the channels under the ice shelf at the point where the ice starts to float.
The match-up indicates that the water flow beneath the grounded ice sheet is responsible for the formation of the channels beneath the floating ice shelf. When the meltwater flowing under the ice sheet enters the ocean beneath the ice shelf, it causes a plume of ocean water to form, which then melts out the vast channels under the ice shelf. Previously, it was thought that water flowed in a thin layer beneath the ice sheet, but the evidence from this study suggests it flows in a more focussed manner much like rivers of water. The way in which water flows beneath the ice sheet strongly influences the speed of ice flow, however, the implications for the future of the ice sheet are yet to be determined.
Dr Anne Le Brocq from the University of Exeter said: “If we are to understand the behaviour of the ice sheet, and its contribution to changes in sea level, we need to fully understand the role of water at the base of the ice sheet. The information gained from these newly discovered channels will enable us to understand more fully how the water system works and, hence, how the ice sheet will behave in the future.”
Channels of this magnitude have been observed before elsewhere, but their formation has been attributed to purely oceanic processes rather than meltwater exiting the grounded ice sheet. Now, with the connection to the meltwater system established, readily obtainable observations from the channels have the potential to shed light on how meltwater flows at the base of an inaccessible kilometre-thick ice sheet.
The study received funding from Natural Environment Research Council (NERC) and the European Space Agency (ESA).
About the University of Exeter
The Sunday Times University of the Year 2012-13, the University of Exeter is a Russell Group university and in the top one percent of institutions globally. It combines world-class research with very high levels of student satisfaction. Exeter has over 18,000 students and is ranked 8th in The Times and The Sunday Times Good University Guide league table, 10th in The Complete University Guide and 12th in the Guardian University Guide 2014. In the 2008 Research Assessment Exercise (RAE) 90% of the University's research was rated as being at internationally recognised levels and 16 of its 31 subjects are ranked in the top 10, with 27 subjects ranked in the top 20.
The University has invested strategically to deliver more than £350 million worth of new facilities across its campuses in the last few years; including landmark new student services centres – the Forum in Exeter and The Exchange on the Penryn Campus in Cornwall, together with world-class new facilities for Biosciences, the Business School and the Environment and Sustainability Institute. There are plans for another £330 million of investment between now and 2016.
For further information and images:
Dr Jo Bowler
University of Exeter Press Office
Office: +44 (0)1392 722062
Mobile: +44(0)7827 309 332
Twitter: @UoE_ScienceNews
j.bowler@exeter.ac.uk
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.exeter.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















