Making better memories
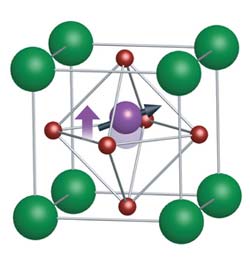
Figure 1: Strontium barium manganite’s properties come from its manganese atoms (purple sphere). Spin (black arrow) endows the material with its magnetic properties, while the displacement of the ion from the center of the cubic lattice (purple arrow) makes it ferroelectric. Oxygen atoms are shown as red spheres and strontium or barium atoms are green. Copyright : 2012 Yasujiro Taguchi<br>
An electric field can displace the cloud of electrons surrounding each atom of a solid. In an effect known as polarization, the cloud centers move away slightly from the positively charged nuclei, which radically changes the optical properties of the solid. Materials that can maintain this polarization, even when the external electric field is removed, are known as ferroelectrics and they could provide a novel route to higher-density memory devices.
“The function of ferroelectric materials is much expanded if they are also magnetic, and if there is a strong coupling between polarization and magnetization,” explains Yasujiro Taguchi from the RIKEN Advanced Science Institute in Wako. Taguchi and his colleagues from RIKEN, and several other Japanese research institutes, recently demonstrated experimentally that the material strontium barium manganite ((Sr,Ba)MnO3) has this rare combination of properties1.
Previous experimental studies on (Sr,Ba)MnO3 did not identify any signs of the ferroelectricity promised by theoretical simulations. The problem was an insufficient ratio of barium to strontium atoms: conventional crystal growth techniques had produced material with only a maximum ratio of 1:4. Taguchi and his colleagues therefore developed a new two-stage growth technique that enabled them to increase the barium content to 50%. By comparing the properties of crystals with different levels of barium content, they identified a transition to a ferroelectric state at a content ratio of between 40 and 45%.
Strontium barium manganite has a so-called perovskite crystal arrangement, which is characterized by a repeating cubic structure (Fig. 1). Manganese atoms are located at the center of the crystal and oxygen atoms are situated in the middle of each of the six sides. Either a strontium or a barium atom sits on each corner of the cube. The spin, or rotation, of an electron in the manganese ions makes the crystal magnetic. Ferroelectricity arises because the manganese ions are displaced slightly from the center of the cube. “Therefore the manganese ions are responsible for both polarization and magnetism and thus a strong coupling between the two emerges,” explains Taguchi.
Materials that are both ferroelectric and have magnetic properties are called multiferroics. The multiferroic materials identified so far have either strong coupling between electricity and magnetism but small polarization, or large polarization with weak coupling. “We have now discovered a multiferroic material that has both [strong coupling and large polarization],” says Taguchi. “These properties are necessary requirements if multiferroic materials are to be applied to devices. One possible example is low-power-consumption memory devices.”
The corresponding author for this highlight is based at the Exploratory Materials Team, RIKEN Advanced Science Institute
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.
Newest articles

A universal framework for spatial biology
SpatialData is a freely accessible tool to unify and integrate data from different omics technologies accounting for spatial information, which can provide holistic insights into health and disease. Biological processes…

How complex biological processes arise
A $20 million grant from the U.S. National Science Foundation (NSF) will support the establishment and operation of the National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences (NCEMS) at…

Airborne single-photon lidar system achieves high-resolution 3D imaging
Compact, low-power system opens doors for photon-efficient drone and satellite-based environmental monitoring and mapping. Researchers have developed a compact and lightweight single-photon airborne lidar system that can acquire high-resolution 3D…





















