Global warming’s biggest offenders
<br>
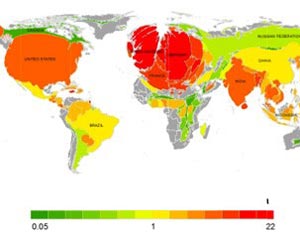
When it comes to global warming, there are seven big contributors: the United States, China, Russia, Brazil, India, Germany and the United Kingdom. A new study published in Environmental Research Letters reveals that these countries were collectively responsible for more than 60 per cent of pre-2005 global warming. Uniquely, it also assigns a temperature change value to each country that reflects its contribution to observed global warming.
The study was conducted at Concordia under the leadership of Damon Matthews, an associate professor in the Department of Geography, Planning and Environment. In a straight ranking, the U.S. is an unambiguous leader, responsible for a global temperature increase of 0.15 C. That’s close to 20 per cent of the observed warming.
China and Russia account for around eight per cent each; Brazil and India seven per cent; and Germany and the U.K. around five per cent each. Canada comes in in 10th place, just after France and Indonesia. Although it may seem surprising that less industrialized countries, including Brazil and Indonesia, ranked so highly, their positions reflect carbon dioxide emissions related to deforestation.
In the study, the research team used a new methodology to calculate national contributions to global warming. It weighted each type of emission according to the atmospheric lifetime of the temperature change it caused. Using data from 1750 onward, the team accounted for carbon dioxide contributions from fossil fuel burning and land-use change, along with methane, nitrous oxide and sulphate aerosol emissions.
Matthews and his colleagues also experimented with scaling the emissions to the size of the corresponding area. Western Europe, the U.S., Japan and India are hugely expanded, reflecting emissions much greater than would be expected based on their geographic area. Russia, China and Brazil stay the same. Taken in this light, the climate contributions of Brazil and China don’t seem so out of line — they are perfectly in proportion with the countries’ landmasses. Of course, Canada and Australia become stick thin, being countries whose geography is much larger than their share of the global warming pie.
Meanwhile, dividing each country’s climate contribution by its population paints a different picture. Amongst the 20 largest total emitters, developed countries occupy the top seven per-capita positions, with Canada falling in third place behind the U.K. and the United States. And in this ranking, China and India drop to the bottom of the list.
Matthews’s study highlights how much individual countries have contributed to the climate problem, as well as the huge disparity between rich and poor with respect to per-person contributions to global warming. Acknowledging these disparities, and then moving to correct them, may be a fundamental requirement for success in efforts to decrease global greenhouse-gas emissions.
NB – Parts of this text appear courtesy of New Scientist magazine.
Source
Cléa Desjardins
Senior Advisor
Media Relations
514-848-2424 ext. 5068
clea.desjardins@concordia.ca
concordia.ca/mediarelations
@CleaDesjardins
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.concordia.caAll latest news from the category: Ecology, The Environment and Conservation
This complex theme deals primarily with interactions between organisms and the environmental factors that impact them, but to a greater extent between individual inanimate environmental factors.
innovations-report offers informative reports and articles on topics such as climate protection, landscape conservation, ecological systems, wildlife and nature parks and ecosystem efficiency and balance.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















