Scientists move a step closer to linking embryos of earth’s first animals to adult form
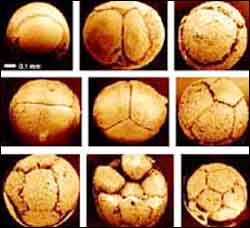
Animal embryos
In 1998, Shuhai Xiao and colleagues reported finding thousands of 600 million year old embryo microfossils in the Neoproterozoic Doushantuo Formation, a fossil site near Weng’an, South China, (Xiao, S., Zhang, Y., and Knoll, A.H., 1998, “Three-dimensional preservation of algae and animal embryos in a Neoproterozoic phosphorite,” Nature, v. 391). Within the egg cases they examined at that time, they discovered animals in the first stages of development – from a single cell to only a few dozen cells. “The cellular preservation is amazing,” says Xiao, assistant professor of geosciences at Virginia Tech.
But what kind of adult would these ancient embryos have hatched into?
In 2000, Xiao’s team reported the discovery of a coral-like animal that might be a candidate for parenthood (Xiao, S., Yuan, X., and Knoll, A.H., 2000, “Eumetazoan fossils in terminal Proterozoic phosphorites?” Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA, v. 97). “It was tubular, not spherical. But in some of the best specimens, we could see that the tube branches and has cross-walls,” Xiao said. “But can it be linked to the embryos?”
Upon examination of more embryos collected from the original site, Xiao’s research team has discovered some embryos that may be at the hatching stage. He will report on this latest finding at the Geological Society of America meeting in Denver Nov. 7-10. “Looking now at these egg cases, we can see clockwise spiral grooves, as if a knife sliced the egg open,” Xiao said. “The embryo was beginning to hatch. When we removed the egg case, we found that the post blastula but pre-hatching embryo at this stage is beginning to transform into a spiral animal. Each such animal had three clockwise spires. After hatching, the spiral organism began to uncoil slightly,” Xiao said. “They look as if they can unwind to a tube structure. We are looking for more evidence, but if that is true, it might link the embryo fossils to the tubular coral-like animal.”
The researchers will slice open a hatched embryo specimen that appears to be unwinding to see if it has cross-walls. “That would indicate it is related to the tubes,” Xiao said. “These organisms lived 600 million years ago – before big animals. This the very first moment of animal evolution preserved in the fossil record.”
The research, “Animal Embryos from the terminal Neoproterozoic Doushantuo Formation: How did they hatch?,” written by Xiao of Virginia Tech’s College of Science, and Chuanming Zhou and Xunlai of the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Paleontology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, will be presented at 1:30 p.m. Wednesday, Nov. 10, in rooms 108/110/112 of the Colorado Convention Center.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.vt.eduAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















