NASA infrared satellite data gives System 96S a fair shot at becoming a tropical cyclone
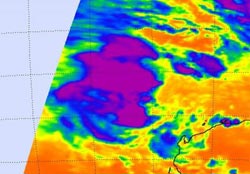
A NASA AIRS instrument infrared image captured on Feb. 9 at 17:47 UTC (12:47 p.m. EST) showed some strong convection and strong thunderstorms (purple) with very cold cloud-top temperatures, around the center of System 96S. Credit: NASA/JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
When Aqua passed over System 96S on Feb. 9 at 17:47 UTC (12:47 p.m. EST), the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument showed some strong convection and strong thunderstorms with very cold cloud-top temperatures around the center of circulation.
Those cloud top temperatures were as cold as or colder than -63 Fahrenheit/-52 Celsius indicating strong convection, strong thunderstorms, and heavy rainfall. The imagery suggests that the convection is consolidating and increasing around the low's center.
Convection is limited on the eastern half of System 96S because of moderate vertical wind shear (winds that can weaken a storm) blowing near 30 knots (34 mph/55 kmh)! That wind shear, however, is expected to weaken and enable the low to strengthen. Another factor that will help System 96S strengthen is the warm sea surface temperatures that it's located in. Sea surface temperatures are estimated near 30 degrees Celsius (86 Fahrenheit). Tropical Cyclones need sea surface temperatures of at least 26.6 Celsius (80 Fahrenheit) to maintain strength or intensify.
At 2300 UTC on Feb. 9, (6 p.m. EST) System 96S had maximum sustained surface winds near 20 to 25 knots (23 mph/ 37 kmh to 29 mph/46 kmh). It was located about 260 miles (418 km) northwest of Barrow Island, Australia near 17.7 South and 112.2 East. Residents of Western Australia are keeping a close eye on this system for development.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















