NASA imagery reveals strength in Tropical Storm Michael's 'arm'
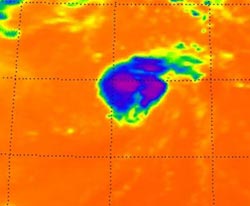
This is Tropical Storm Michael on Sept. 5 at 0611 UTC (2:11 a.m. EDT). Noticed the strongest thunderstorms and coldest cloud top temperatures (purple) around the center of circulation and in a band of thunderstorms to the northeast of the center.<br><br>Credit: NASA JPL, Ed Olsen<br>
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured in infrared image of Tropical Storm Michael on Sept. 5 at 0611 UTC (2:11 a.m. EDT) and noticed the strongest thunderstorms and coldest cloud top temperatures around the center of circulation and in a band of thunderstorms to the northeast of Michael's center.
Those cloud top temperatures were as cold as -63 Fahrenheit (-52 Celsius) and indicated strong thunderstorms with heavy rainfall.
On Sept. 5 at 11 a.m. EDT, Michael had maximum sustained winds near 50 mph (85 kmh). The area of tropical storm force winds have expanded over the last two days and now extend outward up to 60 miles (95 km).
Michael's center was about 1155 miles (1,855 km) west-southwest of the Azores islands, near latitude 28.3 north and longitude 43.3 west. Michael is moving toward the northeast near 6 mph (9 kmh) and is expected to continue in that direction for the next couple of days.
The National Hurricane Center expects the wind shear that has been battering Michael over the last couple of days to relax, which may allow Michael to become a hurricane by Friday, Sept. 7.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.govAll latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















