An Infrared NASA Eye Sees a Weaker System 92B
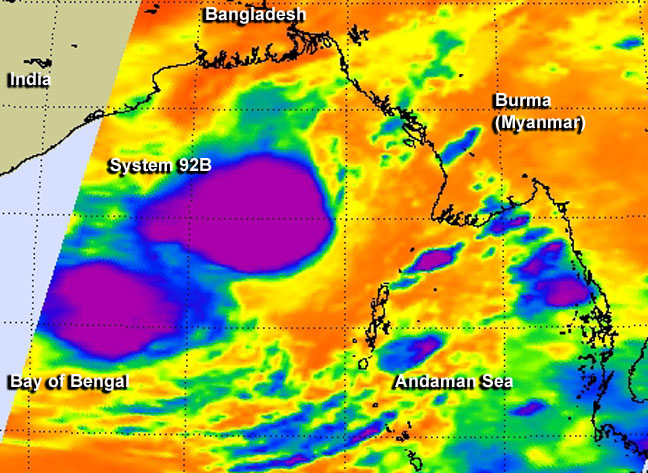
On May 22 at 19:29 UTC/3:29 p.m. EDT, NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 92B and the AIRS instrument saw that the strong thunderstorms over the western quadrant had weakened. Image Credit: NASA JPL/Ed Olsen
On May 22 at 19:29 UTC/3:29 p.m. EDT, NASA's Aqua satellite passed over System 92B and infrared data from the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder (AIRS) instrument and the SSMIS instrument saw patchy deep convection flaring and dissipating over the western portion of a low-level circulation center. Earlier on May 22, the areas of strong thunderstorms were more persistent west of the center of circulation.
The Special Sensor Microwave Imager (SSM/I) and the Special Sensor Microwave Imager Sounder (SSMIS) are satellite passive microwave radiometers. This series of instruments has been carried onboard Defense Meteorological Satellite Program satellites since 1987.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that System 92B has weakened in response to persistent easterly vertical wind shear. The JTWC expects that wind shear to continue for another day.
On May 23 at 02:30 UTC (May 22 at 10:30 p.m. EDT), the center of System 92B was located near 16.2 north latitude and 91.0 east longitude, about 370 nautical miles south of Chittagong, Bangladesh. Maximum sustained winds are between 20 and 25 knots, and minimum central pressure is near 1002 millibars.
JTWC noted “based on the observed weakening trend and considering the potential for redevelopment if vertical wind shear relaxes over the next few days, the potential for the development of a significant tropical cyclone within the next 24 hours is downgraded to medium.”
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/92b-northern-indian-ocean-may-2014/All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Recovering phosphorus from sewage sludge ash
Chemical and heat treatment of sewage sludge can recover phosphorus in a process that could help address the problem of diminishing supplies of phosphorus ores. Valuable supplies of phosphorus could…

Efficient, sustainable and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system for modern power grids
EU project HyFlow: Over three years of research, the consortium of the EU project HyFlow has successfully developed a highly efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective hybrid energy storage system (HESS) that…

After 25 years, researchers uncover genetic cause of rare neurological disease
Some families call it a trial of faith. Others just call it a curse. The progressive neurological disease known as spinocerebellar ataxia 4 (SCA4) is a rare condition, but its…





















