Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

NIST solving a mystery among electrons
When it comes to sleuthing in science, few are better than the intrepid investigators at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). For example, take the “Case of the Stray Electrons.”
NIST researchers have created nanoscale devices that manipulate electrons in order to count them one at a time. Such counting is critical to the development of new fundamental electrical standards. When two electrons are bound in pairs (called Cooper pairs) in a superconductor, they can be man

Turbulence Restrains Itself
Like rapidly flowing gases and liquids, magnetically confined plasmas in tokamaks and related fusion devices exhibit a high degree of turbulence, which can generally destroy the optimal conditions for producing fusion energy. In a deeply encouraging new result, scientists have experimentally confirmed that turbulence can actually limit its own ability to wreak havoc.
Researchers at the DIII-D tokamak at General Atomics have discovered that turbulence generates its own flows that act as a sel
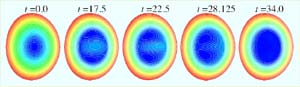
Plasma doughnut currents made hollow, leading to greater efficiency for fusion
Doughnuts of plasma can be coaxed into configurations with hollow current rings, providing practical advantages over conventional “filled doughnut” shapes. Simulations suggest they will allow faster turn-on and greater efficiency of future nuclear fusion power plants.
Toroidal tokamaks, doughnut-shaped experimental fusion reactors, use a complex system of magnetic fields to hold a plasma together. Electrical currents flowing in the plasma itself are essential for making the internal magneti
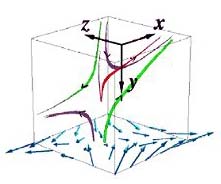
First 3-D Magnetic Reconnection Measurements
In work that promises new insights into the cosmos and fusion-energy production alike, physicists have reported they have made the first three-dimensional laboratory measurements of magnetic reconnection, the main process by which magnetic fields release energy in the universe.
Magnetic reconnection is the phenomenon in which magnetic energy in a plasma is rapidly converted to heat and jets of energetic particles. This process is thought to heat the solar corona, the outer atmosphere of the

X-rays squeeze fuel to generate nuclear fusion energy
Working toward the vision of generating clean energy from nuclear fusion, researchers have successfully imploded fuel capsules by bombarding them with intense x-rays. The results show that the process generates significant fusion and that the implosion method looks capable of generating large-scale energy production.
The process works by bombarding two millimeter (about 1/16th inch) fuel capsules with intense x-rays from Sandia National Laboratories Z-pinch machine. The x-rays, impacting fro

Ultracold gas shows ’lopsided’ properties
Duke University researchers have created an ultracold gas that has the startling property of bursting outward in a preferred direction when released. According to the researchers, studying the properties of the “lopsided” gas will yield fundamental insights into how matter holds itself together at the subatomic level.
Also, the research team leader said their data suggests the possibility that the gas is exhibiting a never-before-seen kind of superfluidity – a property in which matter at ex