Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.

Ultra-Cold Substance Shows Stripes — Behavior Explained
Physicists at Ohio State University may have explained some strange behavior of the ultra-cold material known as Bose-Einstein condensate (BEC).
The new analysis shows that scientists are closer than ever to harnessing BEC to perform useful functions such as quantum computing, said Tin-Lun Ho, professor of physics at Ohio State and the project’s principal investigator.
Ho has pioneered theoretical studies of BEC, an entirely new form of matter that defies description as
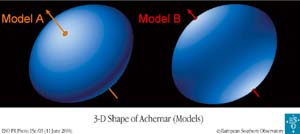
Flattest Star Ever Seen
VLT Interferometer Measurements of Achernar Challenge Stellar Theory
To a first approximation, planets and stars are round. Think of the Earth we live on. Think of the Sun, the nearest star, and how it looks in the sky.
But if you think more about it, you realize that this is not completely true. Due to its daily rotation, the solid Earth is slightly flattened (“oblate”) – its equatorial radius is some 21 km (0.3%) larger than the polar one. Stars are enormous gaseous spheres

Saturn’s winds are variable
A team of astrophysicists at the University of the Basque Country has detected, for the first time ever, changes in Saturn’s winds. The research has merited front page coverage in the scientific magazine, Nature.
The winds blowing around Saturn and Jupiter are special. Unlike those of the rest of the planets, these move in an eastwards direction and are ten times stronger than the earth’s winds. On our planet it is solar radiation which governs the winds, but on the distant planets it is bel

One Thousand ’Wonderful’ Stars Discovered in Centaurus A
First-Ever Census of Variable Mira-Type Stars in Galaxy Outside the Local Group
An international team led by ESO astronomer Marina Rejkuba has discovered more than 1000 luminous red variable stars in the nearby elliptical galaxy Centaurus A (NGC 5128).
Brightness changes and periods of these stars were measured accurately and reveal that they are mostly cool long-period variable stars of the so-called ‘Mira-type’. The observed variability is caused by stellar pulsation.
This is

NASA’s ’Spirit’ Rises On Its Way To Mars
A NASA robotic geologist named Spirit began its seven-month journey to Mars at 1:58:47 p.m. Eastern Daylight Time (10:58:47 a.m. Pacific Daylight Time) today when its Delta II launch vehicle thundered aloft from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla.
The spacecraft, first of a twin pair in NASA’s Mars Exploration Rover project, separated successfully from the Delta’s third stage about 36 minutes after launch, while over the Indian Ocean. Flight controllers at NASA’s Jet Propul

Million-star cluster in nearby galaxy reported
A small, bizarre cluster of a million young stars, enshrouded in thick gas and dust in a nearby dwarf galaxy, has been confirmed by Jean Turner, UCLA professor of physics and astronomy, and her colleagues, in the June 5 issue of the journal Nature.
Turner and her colleagues estimate that the stars are still in the process of forming, and are less than a million years old — extremely young by astronomical standards.
The cluster contains more than 4,000 massive “O” stars, each a milli