Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
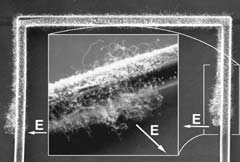
Researchers develop technique that could open doors to faster nanotech commercialization
Engineers at the University of California, Berkeley, have found an innovative way to grow silicon nanowires and carbon nanotubes directly on microstructures in a room temperature chamber, opening the doors to cheaper and faster commercialization of a myriad of nanotechnology-based devices.
The researchers were able to precisely localize the extreme heat necessary for nanowire and nanotube growth, protecting the sensitive microelectronics – which remained at room temperature – just a few mic

ALIS a multi-eyed voyeur in a plasma universe
The Northern Lights are a visible result of physical processes in inner space. By studying the optical signal from the Northern Lights and similar phenomena, we can gain new knowledge about the physics behind them. In the long run such pure research may be of great importance for applications in our future supply of energy and for future space travel.
A dissertation at Umeå University, Sweden, by researcher Urban Brändström at The Swedish Institute of Space Physics, focuses on the constructi

Playing billiards with light provides cheaper lasers
Dutch physicists from Leiden University have made an experimental laser that combines the advantages of two types of laser. With the experimental laser, which generates light in a sort of billiards table with round edges, the researchers have demonstrated that is possible to produce cheaper lasers.
A conventional laser reflects light between two very accurately positioned mirrors, the so-called resonant cavity. The distance between the mirrors determines which wavelength is amplified and th

Rescheduling of some Beagle 2 ’cruise check-out’ tests
The instruments on board ESA’s mission to Mars, Mars Express, are in the process of being tested to verify that they have survived the launch successfully and will work properly. One of these tests on the Mars Express lander, Beagle 2, has been postponed to the first week of July.
This will give engineers extra time to investigate a temporary anomaly that occurred in a memory unit, the so-called “Solid State Mass Memory” (SSMM). The SSMM stores data from the instruments before sending t

Ultrafast laser reveals details about slow electrons
With the help of ultrafast lasers, Dutch researcher Anouk Wetzels from the FOM Institute for Atomic and Molecular Physics has visualised the wave function of slow electrons. The wave function describes how the electron moves around the nucleus of an atom. With this it is possible to directly visualise atomic and even molecular wave functions.
Wetzels used light pulses with a duration of a millionth of a millionth of a second to visualise the wave function of electrons in atoms. With these

Cosmological Gamma-Ray Bursts and Hypernovae Conclusively Linked
Clearest-Ever Evidence from VLT Spectra of Powerful Event
A very bright burst of gamma-rays was observed on March 29, 2003 by NASA’’s High Energy Transient Explorer (HETE-II), in a sky region within the constellation Leo.
Within 90 min, a new, very bright light source (the “optical afterglow”) was detected in the same direction by means of a 40-inch telescope at the Siding Spring Observatory (Australia) and also in Japan. The gamma-ray burst was designated GRB 030329, acco