Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
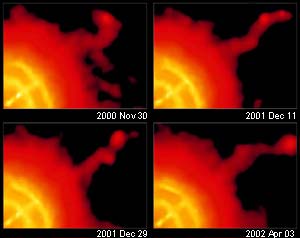
Firehose-like jet discovered in action
An X-ray movie of the Vela pulsar, made from a series of observations by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, reveals a spectacularly erratic jet that varies in a way never seen before. The jet of high-energy particles whips about like an untended firehose at about half the speed of light. This behavior gives scientists new insight into the nature of jets from pulsars and black holes.
Chandra observed the Vela pulsar, a rotating neutron star, 13 times between January 2000 and August 2002. The

Looking Sharp: Images from New Gemini Spectrograph rival view from space
Gemini Observatory’s new spectrograph, without the help of adaptive optics, recently captured images that are among the sharpest ever obtained of astronomical objects from the ground.
Along with the images and spectra acquired during recent commissioning of the Gemini Multi-Object Spectrograph (GMOS) on the 8-metre Gemini South Telescope in Chile, one image is particularly compelling. This Gemini image reveals remarkable details, previously only seen from space, of the Hickson C

The Italian-French interferometer Virgo will be inaugurated on July 23rd
This innovative instrument is aimed to hunt the elusive gravitational waves using extremely sophisticated technological solutions.
On July 23rd in Cascina, near Pisa (Italy), the new Virgo interferometer will be inaugurated. The innovative Virgo gravitational-wave-detector is the outcome of more than ten years of collaborative research and development between the National Institute of Nuclear Physics (Infn, Italy) and the National Scientific Research Centre (Cnrs, France). Letizia Mor

From securing stealth to ensuring health
A material used to protect submarines from sonar detection is the latest technological breakthrough in ensuring the safe and effective dose of ultrasound in medicine. Practitioners and thousands of patients in physiotherapy departments worldwide will benefit from the latest technology, which will ensure a step forward in the reliability of delivered ultrasound treatment.
The material forms a key component in a novel desk-top ultrasound power meter developed by the UK’s national standards lab

Astronomers find Paschen in the bar
An international team of astronomers have used a unique instrument on the 8-m Gemini South Telescope to determine the ages of stars across the central region of the barred spiral galaxy, M83. Preliminary results provide the first hints of a domino model of star formation where star formation occurs in a time sequence, driven by the movements of gas and stars in the central bar.
The new instrument, called CIRPASS, simultaneously produces 500 spectra, taken from across the whole region of inte

Seizing the moment: improving control of quantum dots
A light bulb isn’t very useful without a reliable on/off switch. The same holds true for quantum dots. These ultra tiny electronic nanostructures someday may serve as the ones and zeros used by a superfast quantum computer, but first physicists need to refine their ability to turn quantum dots “on” and “off.”
In the June 23, 2003, on-line issue of Applied Physics Letters, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the National Renewal Energy Laborato