Latest News

Cassava mealybug control : parasitoid wasps hold the kairomone key
The mealybug Phenacoccus herreni feeds on cassava plant sap, inducing shrivelling. It causes extensive damage in cassava growing areas in South America. However, it can be parasitized by two wasps, Acerophagus coccois and Aenasius vexans which act out a ritual to recognize and select the individuals they are going to parasitize. A wasp moves from one side to the other of a potential victim, investigating it by palpation with their antennae. Once this “drumming and turning” procedure completed, the wa
Study refines breast cancer risks
Large scale study spells out links with pregnancy and miscarriage.
Childless women are at a higher risk of developing breast cancer, confirms one of the largest studies on reproductive factors and the disease, but those who suffer miscarriages are not. Researchers are pinning down key risk factors in the hope of working out exactly how they increase susceptibility.
How pregnancy and abortion alter women’s chance of developing breast cancer has been the subject of conflictin
<i>Goldfinger</i> held grain of truth
Our skin takes its oxygen straight from the air.
The James Bond movie Goldfinger spawned the urban myth that a person can suffocate if air cannot reach their skin. But the plot contains a grain of truth, new research reveals – our skin gets its oxygen from the atmosphere, not the blood.
Air supplies the top 0.25-0.4 mm of the skin with oxygen, dermatologist Markus Stücker of the Ruhr-University in Bochum, Germany, and his colleagues have found. This is almost 10 times
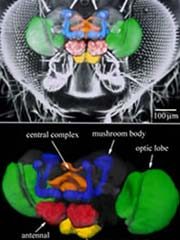
Standard fly brain sized up
Average insect brain should help spot defects and their causes.
Two hair’s breadths long and five across – that’s the average capacity of a fly’s brain, German researchers have calculated. They hope to set a benchmark for crania by which oddballs can be judged.
Although it is a creature of little brain, the fruit fly ( Drosophila ) is popular with geneticists. Researchers often study flies that lack a particular gene, looking for flaws that might hint at

Women’s dissatisfaction with body image greater in more affluent neighbourhoods
The more affluent the area in which she lives, the more dissatisfied a woman is likely to be with her body image, indicates research in the Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health.
The researchers carried out a random telephone survey of 895 women aged 25 to 56. The women lived in 52 neighbourhoods in the provinces of Alberta, Ontario, and Quebec in Canada. The survey was designed to cover differing social and income brackets. National census data were then used to track the overall af

"Suicide gene" injection shrinks cancer growth
Injectable “suicide gene” therapy may be a highly effective way of preventing colon cancer from spreading (metastasising), finds research in Gut. Human colon cancer carries a high risk of death because it is often not found in the early stages and readily spreads to the liver, but also the lungs and throughout the abdominal cavity (peritoneum).
And the suicide gene treatment seems to be just as effective when injected beneath the skin as it is when introduced directly into the tumour site, t