Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.

Shadow proteins in thymus – Clues to how immune system works?
Findings could lead to new understanding of diabetes, Crohn’s, and more
Researchers at Joslin Diabetes Center, Harvard Medical School, and other institutions have identified the function of a protein, dubbed aire, that is critical to helping immune cells learn to recognize–and avoid attacking–the far-flung organs and tissues of the body. The protein appears to work by turning on in the thymus, which lies beneath the breast bone, the production of a wide array of proteins from the bo

Selfing DNA prevents genomes from mixing
Genomes of multicellular organisms are one of the greatest mysteries of biology. The more is discovered about them, the more questions are to be answered. One of such questions is connected with the size of a genome. As is known since the middle of the 20th century, the level of organization of an organism does not depend on the genome size, i.e., on the amount of DNA in the nucleus of a cell. Sometimes, a primitive organism contains much more DNA than a mammal. For example, the genome of certain amo

Purdue corrals new Trojan horse to replace wayward genes in mice
A research team at two Midwest universities has developed a new way to genetically alter cells in living mice, offering new possibilities in the war against cancer and other diseases.
Using a modified virus as a Trojan horse, a team led by Purdue University’s David Sanders has found a promising system to deliver genes to diseased liver and brain cells. By placing helpful genetic material within the outer protein shell of Ross River Virus (RRV), Sanders’ team was able to alter the
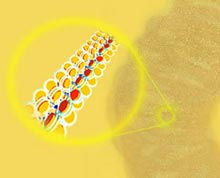
How a master protein remodels chromosomes to orchestrate gene expression
A team led by Terumi Kohwi-Shigematsu of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory’s Life Sciences Division has demonstrated that SATB1, a protein crucial to the development of the immune system, works by forming a network in the cell nucleus, attaching chromatin to the network structure at specific sites, and orchestrating remodeling of the chromatin over long distances to regulate gene expression.
“SATB1 determines when and how the genes are read — when they are activated and when they are
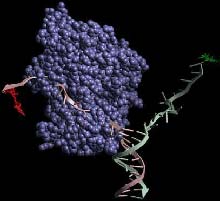
DNA unzipping found to take at least two proteins, not one alone
Using an optical fluorescence microscope to monitor enzyme activity, researchers at three universities have solved a long-running mystery. It takes at least two proteins, working in an unstable tandem, to unzip two strands of DNA.
Their newly designed approach, which focuses on the activity of single molecules, also showed — for the first time — that if one protein falls away, the process stops. Unless another climbs aboard, DNA reverts to its zipped state.
The technique, which o

RRF Recycles Form, Not Exact Function
Ribosome Recycling Factor Mimics Shape, But Not The Functions of Transfer RNA
RRF Protein Offers Potential Target for New Antibiotics
The fact that ribosome recycling factor (RRF) looks a lot like transfer RNA (tRNA) has not been lost on scientists. After all, both molecules are an important part of a bacteria’s ability to create new proteins. Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the University of Southern California, Santa Cruz, however, hav