NASA Releases Images of M-class Solar Flare
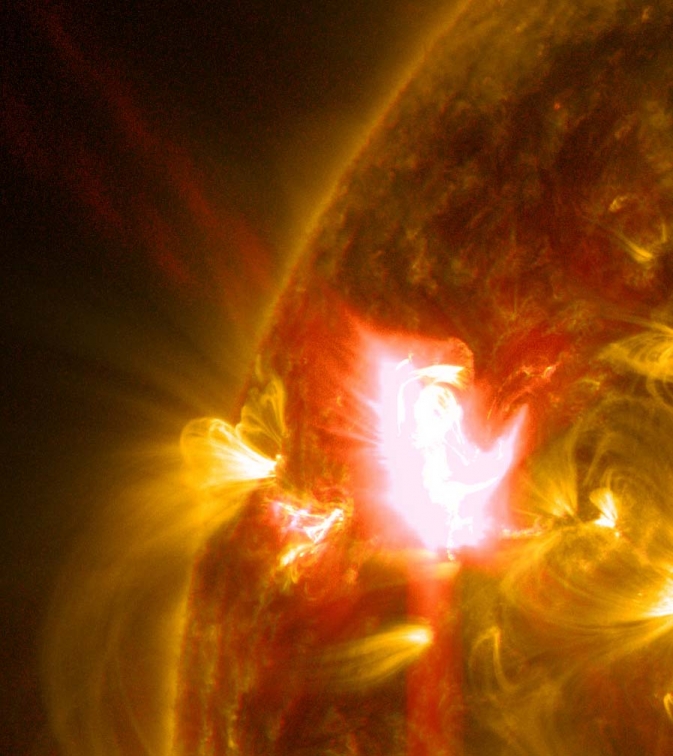
A mid-level flare, an M6.5, erupted from the sun on April 2, 2014, peaking at 10:05 a.m. EDT. This image from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory shows the flare in a blend of two wavelengths of extreme ultraviolet light: 131 Angstroms and 171 Angstroms, colorized in yellow and red, respectively. Image Credit: NASA/SDO/Goddard Space Flight Center
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however — when intense enough — they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may impact Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
This flare is classified as an M6.5 flare. M-class flares are ten times less powerful than the most intense flares, which are labeled X-class. The number after the M provides more information about its strength. An M2 is twice as intense as an M1, an M3 is three times as intense, etc.
Updates will be provided as needed.
Related Links
› Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Space Weather
› View Other Past Solar Activity
Karen C. Fox
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions…

An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of a powerful epigenetic editing technology, which unlocks the ability to precisely program chromatin modifications. Understanding how…

NASA selects UF mission to better track the Earth’s water and ice
NASA has selected a team of University of Florida aerospace engineers to pursue a groundbreaking $12 million mission aimed at improving the way we track changes in Earth’s structures, such…





















