Staphylococcus aureus: A new mechanism involved in virulence and antibiotic resistance
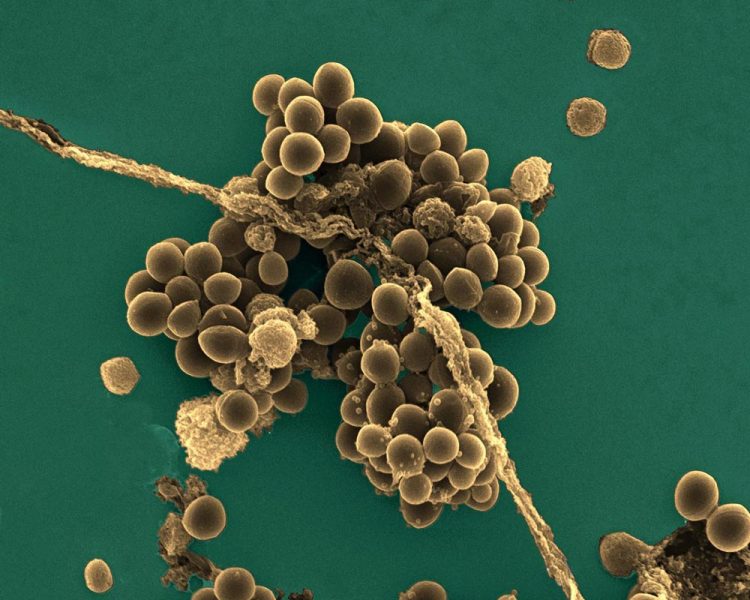
These are Staphylococcus aureus cells ('golden staph') observed by scanning electron microscopy Credit: © Institut Pasteur/Mélanie Falord and Tarek Msadek -- Colorization by Jean-Marc Panaud
Staphylococcus aureus is part of the natural skin flora, preferentially colonizing external mucosa in 30 to 50% of the population, healthy carriers who develop no symptoms. But it is also a major human pathogen, causing diseases ranging from skin lesions (boils, impetigo, etc.) to endocarditis, acute pneumonia, osteomyelitis or sepsis.
It is the leading Gram-positive bacterium responsible for nosocomial infections (hospital acquired infections). The most dangerous strains are those that display resistance to multiple antibiotics. This is the case of MRSA[1], resistant to Meticillin, widespread in hospitals and posing a major public health concern.
The Signaling and Pathogenesis of Staphylococci team, led by Tarek Msadek, a researcher in the Biology of Gram-positive Pathogens Unit at the Institut Pasteur (CNRS ERL 3526), is studying bacterial responses to environmental variations and their role in Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis and host interactions.
These responses are often genetically controlled by so-called “two-component” systems. During the study of one of these systems, WalKR, essential for bacterial survival, they characterized an additional component, SpdC, a membrane protein whose role was unknown.
This component interacts with the WalKR system to control its activity and its absence leads to a strong decrease in virulence, biofilm formation (bacterial aggregates), and resistance to certain antibiotics.
These results suggest that inhibition of SpdC could be used as an approach to combat S. aureus infections and understand the mechanisms involved in its transition from commensal to pathogen.
###
[1] Meticillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Health and Medicine
This subject area encompasses research and studies in the field of human medicine.
Among the wide-ranging list of topics covered here are anesthesiology, anatomy, surgery, human genetics, hygiene and environmental medicine, internal medicine, neurology, pharmacology, physiology, urology and dental medicine.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…





















