Study gives clues to the origin of Huntington's disease, and a new way to find drugs
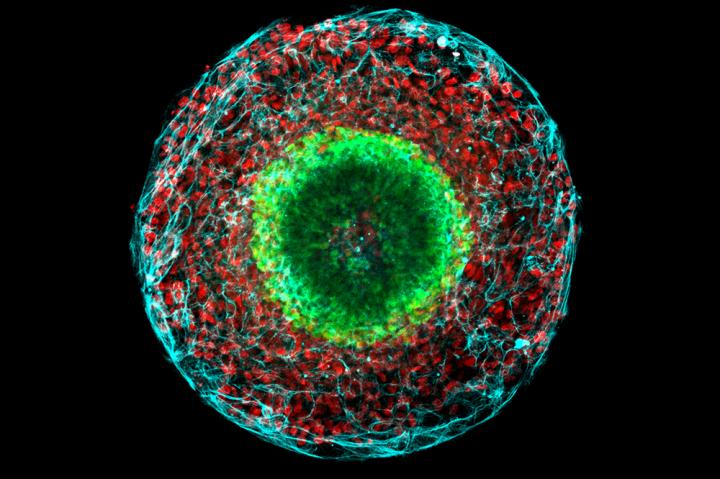
Developmental diseases can now be studied with new technology involving tiny brain models called neuruloids, shown here. Credit: Laboratory of Stem Cell Biology and Molecular Embryology at The Rockefeller University Usage Restrictions: Image may only be used to illustrate research described in the accompanying release.
Developed in the lab of Ali Brivanlou, the Robert and Harriet Heilbrunn Professor, the system uses neuroloids–tiny, three-dimensional tissue cultures that serve as models for whole organs.
The researchers create these cell clumps from human embryonic stem cells and manipulate them in the lab to study how developmental diseases arise.
Previous work in the Brivanlou lab found evidence that the disease arises in young neurons; but this latest study takes the developmental timeframe back even further, to the step in the brain's development when cellular uniformity gives way to the emergence of particular structures, a process called neurulation.
When the researchers introduced into neuroloids a mutation known to cause Huntington's, it consistently caused dramatic effects with abnormally shaped tissue structures. “Something's collapsed,” Brivanlou says.
The researchers have started using the technology to screen for drugs that prevent these abnormalities, an approach they hope will provide a powerful alternative to similar work being done in animal models.
“This technology really opens a door toward identifying that mechanisms that govern brain development, understanding how they go awry in disease, and testing drugs that set these mechanisms back on the right course,” says Brivanlou.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Microscopic basis of a new form of quantum magnetism
Not all magnets are the same. When we think of magnetism, we often think of magnets that stick to a refrigerator’s door. For these types of magnets, the electronic interactions…

An epigenome editing toolkit to dissect the mechanisms of gene regulation
A study from the Hackett group at EMBL Rome led to the development of a powerful epigenetic editing technology, which unlocks the ability to precisely program chromatin modifications. Understanding how…

NASA selects UF mission to better track the Earth’s water and ice
NASA has selected a team of University of Florida aerospace engineers to pursue a groundbreaking $12 million mission aimed at improving the way we track changes in Earth’s structures, such…