Clues to gene expression in Cystic Fibrosis will guide research

Results from a French clinical trial published today in BMC Medicine show how a small percentage of CF sufferers with a rare genetic stop mutation responded positively to gentamicin treatment.
Aleksander Edelman and Isabelle Sermet-Gaudelus of Faculté de Médicine Necker in Paris led collaborators from several French institutions studying how the antibiotic gentamicin affected CF patients with a stop mutation. The team used a dual reporter gene assay first in vitro and then in CF patients. The study found that a small subgroup of patients with the Y122X mutation, found mainly in inhabitants of Reunion island, responded to gentamicin treatment.
Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the gene that encodes the Cystic Fibrosis Transmemrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) protein. Over 1500 mutations have been described since this gene’s discovery. Premature stop mutations, which includeY122X, are found in around 10% of CF patients. Gentamicin reversed stop codons in the Y122X gene, and helped restore the CFTR protein, improving patients’ respiration.
Gentamicin itself may not be an ideal drug option, as it may cause serious side effects for some patients, including ear and kidney damage. The authors suggest that other drugs, such as amikacin or PTC124, with a comparable mode of action and fewer side effects, may have treatment potential. The in vitro method used to predict the trial’s outcome could be a first step to developing treatments effective for patients with CF and other diseases where premature stop codons play a role.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.biomedcentral.com/bmcmed/All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
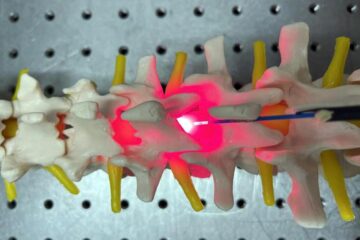
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….