Safe is sexy

Females prefer burrows
The signal is an arched wall of sand called a hood which courting males of the fiddler crab Uca musica build at the entrances to their burrows on sand flats in Panama. Males have one very large claw that they wave to attract females to their burrows and females visit several males before choosing a mate by staying with a male in his burrow. These small crabs are at great risk of predation from ever-present shore birds. When moving between burrows they reduce this risk in part by running to objects that provide cover.
Christy, from the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute (STRI) in Panama, Julia Baum, an undergraduate at McGill University, and STRI researcher Pat Backwell thought that hoods might attract females because they look like objects that provide temporary hiding places. As reported recently in the journal Animal Behaviour (66: 89-94) they found ample support for this idea. They showed that female fiddler crabs, including species that do and do not build structures, are equally attracted to hoods and other objects to escape predation. They then replaced males’ hoods with stones, shells, pieces of wood and hood replicas and tested their attractiveness to females. Females found all males to be equally attractive regardless of what kind of object was at their burrow. The researchers conclude that some male courtship signals may be designed to keep females safe as they search for a mate, not to advertise the quality of the signaler and more generally, that a species’ ecology can favor responses that in turn become incorporated into courtship.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.si.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
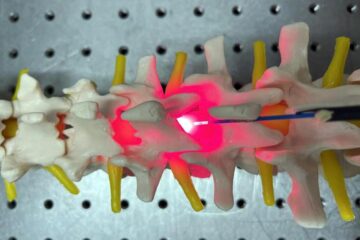
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….