MU researchers find missing link in plant defense against fungal disease

Scientists at the University of Missouri report on a discovery in a key component in the signaling pathway that regulates the production of phytoalexins to kill the disease-causing fungus Botrytis cinerea.
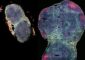
“When the mustard plant Arabidopsis detects the fungus Botrytis cinerea, it produces a phytoalexin, called camalexin, in response,” said Shuqun Zhang, professor of biochemistry and senior author of the study. “Camalexin acts as sort of an antibiotic against the specific fungus, allowing the plant to successfully defend itself.”
In previous work, Zhang and his colleagues showed a signaling pathway, known as MAPK cascade, triggers the transcription activation of genes that make camalexin in Arabidopsis. This study shows that the target of this signaling cascade is the WRKY33 transcription factor.
Arabidopsis plants lacking the gene are unable to synthesize camalexin and are more susceptible to the Botrytis cinerea fungus.
The finding provides an important missing link in the chain of molecules that tells the plant to mount an appropriate defense against an invading microbe.
“Phytoalexins are one important way plants defend themselves naturally against pathogens. Knowing how plants regulate this defense response may allow us to naturally enhance pathogen tolerance in plants,” Zhang said.
The study, titled “Phosphorylation of a WRKY transcription factor by two pathogen-responsive MAPKs drives phytoalexin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis,” is highlighted in the April 15 online early edition publication of The Plant Cell. The paper's co-authors include Guohong Mao and Xiangzong Meng from the University of Missouri; and Zuyu Zheng and Zhixiang Chen from Purdue University. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.missouri.eduAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
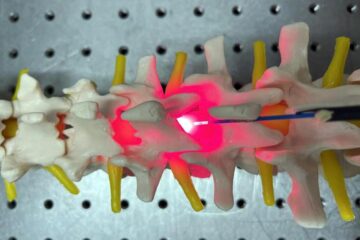
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….