Hydra Can Modify Its Genetic Program
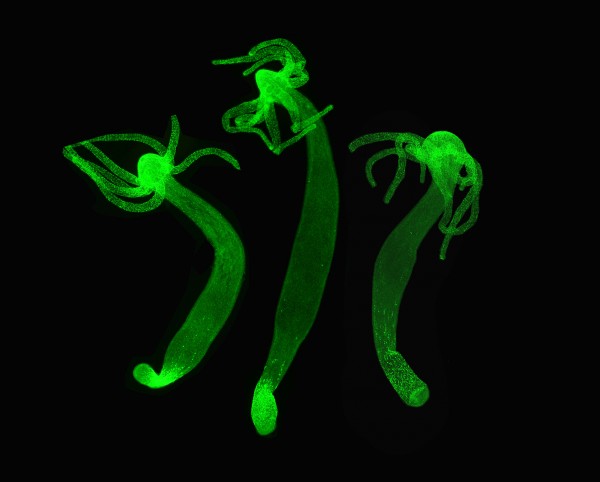
© Brigitte Galliot The nervous system of about 1 cm-long Hydra revealed here with a fluorescent green marker.
Researchers at the University of Geneva (UNIGE), Switzerland, have discovered how: cells of the epithelial type modify their genetic program by overexpressing a series of genes, among which some are involved in diverse nervous functions.
Studying Hydra cellular plasticity may thus influence research in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. The results are published in Philosophical Transactions, the journal of the Royal Society.
The freshwater Hydra is endowed with an extraordinary power of regeneration, discovered by the Swiss naturalist Abraham Trembley more than 250 years ago.
The group of Brigitte Galliot, professor at the Department of Genetics and Evolution of the Faculty of Science of UNIGE, has studied the stem cells functioning and cellular plasticity of the polyp: «its nervous system regulates in particular contraction bursts, feeding behavior, moving or swimming. If the stem cells responsible for its renewal are depleted, the Hydra can still develop, even when all its neurons have disappeared. We wanted to understand how this is possible.»
Enhancing other cells’ sensing ability
The researchers compared gene expression at various positions along the body axis in polyps devoid or not of their nervous stem cells. They observed a modification of the genetic program in animals depleted of these cells: «we identified 25 overexpressed genes in epithelial cells, the cells forming the Hydra’s coating tissues. Some of these genes are involved in diverse nervous functions, such as neurogenesis or neurotransmission», says Yvan Wenger, co-first author of the article.
«Epithelial cells do not possess typical neuronal functions. However, Hydra’s loss of neurogenesis induces epithelial cells to modify their genetic program accordingly, indicating that they are ready to assume some of these functions.
These “naturally” genetically modified epithelial cells are thus likely to enhance their sensitivity and response to environmental signals, to partially compensate for the lack of nervous system», explains Wanda Buzgariu, co-first author of the article. The detail of these new functions remains to be discovered, as well as how epithelial cells proceed to overexpress these genes and thus adapt their genetic program.
Cellular plasticity maintains youth
Studying Hydra’s cellular plasticity may be relevant in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. Indeed, some of the genes identified in this animal play an important role in cellular reprogramming or in neurogenesis in mammals. The researchers therefore wonder: would it be possible to restore sensing or secretion functions from other cell types, when some neurons degenerate?
This study also allows to go back to the origins of nervous systems. Epithelial cells most probably preceded nerve cells, performing some of their functions, although in a much slower way. «The loss of neurogenesis in Hydra may provide an opportunity to observe a reverse evolutive process, because it sheds light on a repressed ancestral genetic toolkit. An atavism of epithelial cells, when they most probably also possessed proto-neuronal functions», concludes Brigitte Galliot.
Contact Information
Julie Michaud
Communication Manager
Julie.Michaud@unige.ch
Phone: +41 22 379 77 96
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…