A New Role for Cytokinin Plant Hormones

When plants, including crops, are exposed to environmental stresses such as drought or high salinity, abscisic acid (ABA), a stress-responsive hormone is synthesized to induce a protective response.
At the same time, the content of another plant hormone, cytokinin (CK), which is involved in regulation of plant growth, such as promotion of cell division or inhibition of senescence, is reduced.
This phenomenon suggests that CK might play an essential role in regulation of plant adaptation to environmental stresses. However, how CK regulates plant response to stresses and how stresses regulate CK metabolism; these questions required answers.
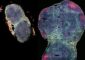
The Signaling Pathway Research Unit discovered that mutual regulation mechanism between CK and ABA affects the plant’s adaptation to stressors. The authors found that the CK-deficient Arabidopsis plants with reduced CK levels exhibited a strong stress-tolerant phenotype that was associated with improved cell membrane integrity and ABA hypersensitivity.
Additionally, using Arabidopsis the authors provided evidence that drought and salt stresses reduce the levels of the bioactive CKs by alteration of expression of CK metabolic genes. Taken together, the group suggested that because of the reduction in CK content under drought and salt stresses, the inhibitory effect of the CK regulatory network on the expression of stress-responsive genes is alleviated, leading to enhanced stress tolerance. CK biology, therefore, represents a promising tool for agronomy and can provide multiple biotechnological strategies to maintain agriculture in a sustainable fashion.
These results were published in the June 2011 edition of The Plant Cell.
Contacts
Plant Science Center, RIKEN
Dr. Lam-Son Phan Tran (Unit Leader):
TEL 045-503-9593, FAX 045-503-9591
Dr. Rie Nishiyama (Researcher):
TEL 045-503-9572, FAX 045-503-9591
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….