Earthquake researchers finalists for supercomputing prize
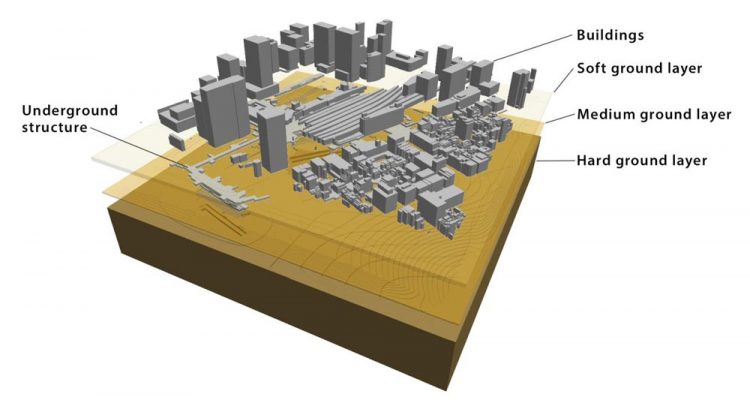
Various layers of the earth plus buildings on top of and within them behave differently during an earthquake. Interactions between these layers expound complexity of earthquake models. Credit: 2018 Earthquake Research Institute, The University of Tokyo. Usage Restrictions: Related to this news release
A team of researchers from the Earthquake Research Institute, Department of Civil Engineering and Information Technology Center at the University of Tokyo, and the RIKEN Center for Computational Science and RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project in Japan were finalists for the coveted Gordon Bell Prize for outstanding achievements in high-performance computing.
Tsuyoshi Ichimura together with Kohei Fujita, Takuma Yamaguchi, Kengo Nakajima, Muneo Hori and Lalith Maddegedara were praised for their simulation of earthquake physics in complex urban environments.
Earthquakes are a huge problem in many places around the world including, famously, Japan. They can be devastating and Ichimura's team use coding prowess with the power of supercomputers to generate models for disaster mitigation and response.
Realistic earthquake simulations are difficult due to wide-ranging physical phenomena operating at different scales. This complex problem led the team to devise novel strategies involving artificial intelligence (AI) to model earthquakes in urban centers with a high degree of accuracy.
“In the field of computer science there is a big gap between AI and physics-based simulations,” said Ichimura. “We felt there was scope to enhance performance of our simulation by bridging this gap. And that feeling turned out to be true.”
Their mixed-methodology approach utilized AI and varying degrees of mathematical precision to create a completely new code for the simulation – with unprecedented efficiency. This new code achieved an almost fourfold increase in speed over the team's previous incarnation.
Traditionally, physical simulations require great numerical accuracy to obtain results that correspond well with observed reality. To achieve this precision requires a lot of computing time, which consumes a great amount of power. What makes this new method unique is how the AI component of the system learns where precision is most useful and where it can be reduced without sacrificing overall accuracy, so the simulation can run in less time than if it lacked the AI.
The team's code ran on the state-of-the-art Summit supercomputer at the Oak Ridge National Laboratory in the U.S. The researchers made this code adaptable for other uses and scalable for use on different computer systems such as the K computer at RIKEN and Piz Daint at the Swiss National Supercomputing Centre.
“Our code is an entirely new kind of problem solver, which is a frontier in this field,” concludes Ichimura. “We expect this new code will find its way into a new generation of physical simulators. We hope this helps people better understand, predict and prepare for earthquakes.”
###
Paper details
Tsuyoshi Ichimura, Kohei Fujita, Takuma Yamaguchi, Akira Naruse, Jack C. Wells, Thomas C. Schulthess, Tjerk P. Straatsma, Christopher J. Zimmer, Maxime Martinasso, Kengo Nakajima, Muneo Hori, Lalith Maddegedara, A Fast Scalable Implicit Solver for Nonlinear Time-Evolution Earthquake City Problem on Low-Ordered Unstructured Finite Elements with Artificial Intelligence and Transprecision Computing, SC'18 Proceedings of the International Conference for High Performance Computing, Networking, Storage, and Analysis, Article No. 49, 2018.
Support and funding
These results were obtained using the Summit supercomputer at Oak Ridge Leadership Computing Facility, a U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science user facility at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Piz Daint at Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (CSCS) and K computer at RIKEN Center for Computational Science (R-CCS, proposal numbers: hp170249, hp180217). The research received support from Post K computer project (Priority Issue 3 – Development of integrated simulation systems for hazards and disasters induced by earthquakes and tsunamis) and Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (18H05239, 26249066, 25220908, and 17K14719).
Related links
Earthquake Research Institute – http://www.
Graduate School of Engineering – http://www.
Department of Civil Engineering – http://www.
Researcher contact
Associate Professor Tsuyoshi Ichimura
Earthquake Research Institute, The University of Tokyo, 1-1-1 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-0032, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-5692
Email: ichimura@eri.u-tokyo.ac.jp
Press contact
Mr. Rohan Mehra
Division for Strategic Public Relations, The University of Tokyo, 7-3-1 Hongo, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 133-8654, JAPAN
Tel: +81-3-5841-0876
Email: press-releases.adm@mail.u-tokyo.ac.jp
About the University of Tokyo
The University of Tokyo is Japan's leading university and one of the world's top research universities. The vast research output of some 6,000 researchers is published in the world's top journals across the arts and sciences. Our vibrant student body of around 15,000 undergraduate and 15,000 graduate students includes over 2,000 international students. Find out more at http://www.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Information Technology
Here you can find a summary of innovations in the fields of information and data processing and up-to-date developments on IT equipment and hardware.
This area covers topics such as IT services, IT architectures, IT management and telecommunications.
Newest articles

ONe nova to rule them all
Astronomers have proposed a new theory to explain the origin of phosphorus, one of the elements important for life on Earth. The theory suggests a type of stellar explosion known…

High-efficiency hollow-core fiber optic cable helps medical procedures
Recently, a research group led by Prof. JIANG Haihe from Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) designed a 6-hole micro-structure anti-resonant air-core fiber (AR-HCF) with a larger core diameter…

Tauonium: the smallest and heaviest atom with pure electromagnetic interaction
The hydrogen atom was once considered the simplest atom in nature, composed of a structureless electron and a structured proton. However, as research progressed, scientists discovered a simpler type of…