Solar houses scientifically evaluated
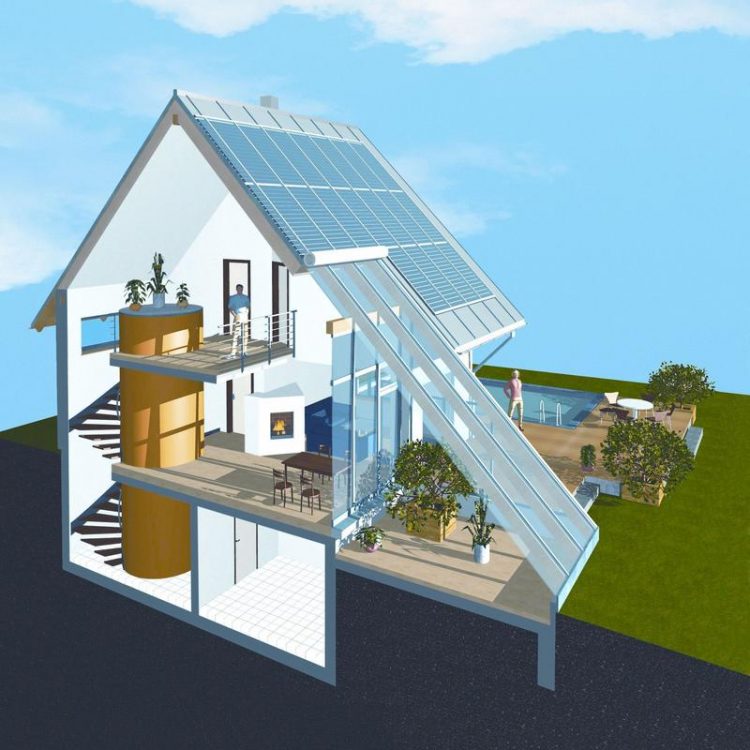

Diagram of a solar house. © Sonnenhaus-Institut e.V.
Primary energy demand and costs in comparison
In order to scientifically evaluate the buildings, the scientists developed a new simulation method in the research project HeizSolar. With this new method, experts can analyse different solar house constellations in terms of primary energy demand and costs.
For example, the researchers varied the solar savings fraction between 50 and 100 per cent, and combined the data with different efficiency house standards. They also compared the solar house concept with other low-carbon heat supply concepts, such as using pellets or logs to meet heating requirements.
The foundation for the development of the simulation method was formed by evaluations of three multi-family and six single-family homes. These conceptually different solar houses were measured throughout several heating seasons. Based on the monitoring results and the gained operational experience, the scientists then derived optimisation suggestions for the collector layouts and the storage technologies.
The research project HeizSolar was carried out under the leadership of the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems. Participating institutes included Sonnenhaus-Institut, the Ilmenau University of Technology, and Solar- und Wärmetechnik Stuttgart.
You found all informations about the BINE Projektinfo brochure entitled “Assessing solar houses in energy and economic terms” here:
http://www.bine.info/en/press/press-releases/press/pressemitteilung/sonnenhaeuse…
Uwe Milles/Birgit Schneider
presse(at)bine.info
About BINE Information Service
Energy research for practical applications
The BINE Information Service reports on energy research topics, such as new materials, systems and components, as well as innovative concepts and methods. The knowledge gained is incorporated into the implementation of new technologies in practice, because first-rate information provides a basis for pioneering decisions, whether in the planning of energy-optimised buildings, increasing the efficiency of industrial processes, or integrating renewable energy sources into existing systems.
About FIZ Karlsruhe
FIZ Karlsruhe – Leibniz Institute for Information Infrastructure is a not-for-profit organization with the public mission to make sci-tech information from all over the world publicly available and to provide related services in order to support the national and international transfer of knowledge and the promotion of innovation.
Our business areas:
• STN International – the world’s leading online service for research and patent information in science and technology
• KnowEsis – innovative eScience solutions to support the process of research in all its stages, and throughout all scientific disciplines
• Databases and Information Services – Databases and science portals in mathematics, computer science, crystallography, chemistry, and energy technology
FIZ Karlsruhe is a member of the Leibniz Association (WGL) which consists of 87 German research and infrastructure institutions.
http://www.bine.info/en – BINE Informationsdienst
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles
Exploring the Asteroid Apophis With Small Satellites
In five years’ time, a large asteroid will fly very close to Earth – a unique opportunity to study it. Concepts for a national German small satellite mission are being…
First model of the brain’s information highways developed
Our human brain is not only bigger and contains more neurons than the brains of other species, but it is also connected in a special pattern: Thick bundles of neurons…

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…





















