Gazing into the flames of ionic winds
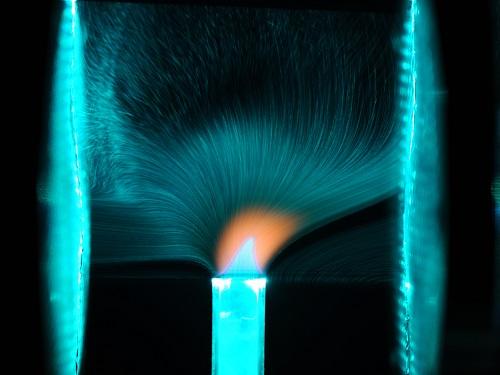
The researchers acquired incredible images, such as this one, showing a jet flame being affected by a 16-kV electric field between two electrodes. Credit: © 2017 Minsuk Cha
Min Suk Cha and coworkers had developed a theoretical model explaining how ions in a flame respond to electric fields. For their latest work, the researchers ejected a mixture of methane and air through a jet flame nozzle positioned between two electrodes.
They illuminated the flame using an argon-ion laser and detected the scattered light in order to trace the motion of individual particles through the flame–a technique called particle image velocimetry or PIV. To improve this visualization, they had to add to the flame reflective seeding particles made from titanium oxide and oil.
“The particle seeding to the ambient flame was quite difficult,” says Cha. “We used a smoke generator, but we had to control the timing of the smoke generation very carefully so that we didn't disturb the main flow. It was a time-consuming step requiring a lot of patience.”
The researchers acquired images that reveal unprecedented details of how flame dynamics respond to electricity. When they used a DC field, the flame visually bent towards the negative electrode because positive ions (which vastly outnumber negative ions in the flame) were attracted that way (see image).
Counterintuitively, however, the ionic wind blew toward both electrodes, indicating an important role for negative ions. In an AC field, the ionic wind dynamics depended on the applied AC frequency, though only at low frequencies. These ionic winds could influence the combustion process by allowing a controlled redistribution of heat and combustion products by convection.
Cha says he hopes that this work could have a very positive impact on the future design of flame-generating machinery. Most importantly, it wouldn't require the building of completely new industrial equipment, as Cha explains:
“The beauty of this method is that it can be retrofitted–it can be added in as an active control method for any pre-existing combustion system. Depending on the system configuration and the type of combustion that we need to control, we could use our knowledge and understanding to work out the appropriate locations of electrodes and choose the best operational parameters, such as voltage or frequency.”
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Power and Electrical Engineering
This topic covers issues related to energy generation, conversion, transportation and consumption and how the industry is addressing the challenge of energy efficiency in general.
innovations-report provides in-depth and informative reports and articles on subjects ranging from wind energy, fuel cell technology, solar energy, geothermal energy, petroleum, gas, nuclear engineering, alternative energy and energy efficiency to fusion, hydrogen and superconductor technologies.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…





















