NASA sees Tropical Cyclone Nathan moving south and strengthening
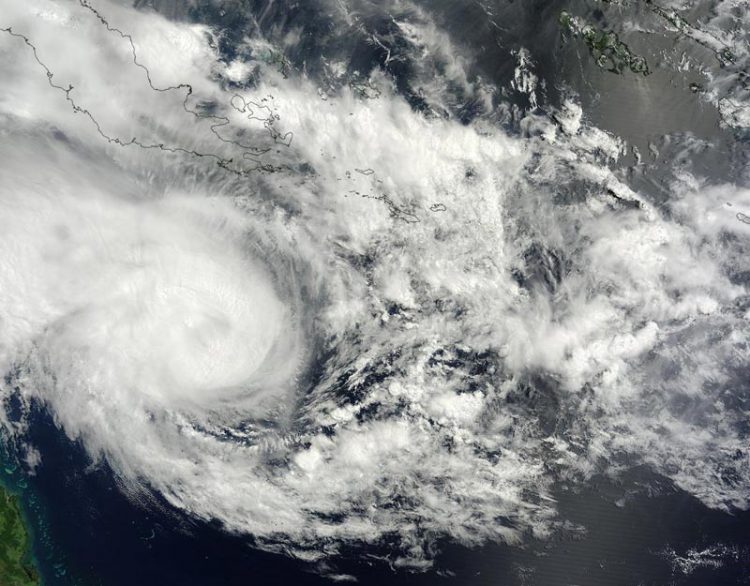

NASA's Terra satellite captured this visible image of Tropical Cyclone Nathan east of the Queensland coast on March 16 at 0:00 UTC. Credit: NASA Goddard MODIS Rapid Response
At 0900 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), Tropical cyclone Nathan's maximum sustained winds were near 55 knots (63.2 mph/102 kph) and the storm was consolidating and organizing.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) forecasters expect Nathan to strengthen to 70 knots in two days.
Nathan was centered near 14.3 south latitude and 150.2 east longitude, about 298 nautical miles east-northeast of Cairns, Australia. It was moving to the southeast at 5 knots (5.7 mph/9.2 kph).
JTWC noted satellite imagery revealed “a slowly-consolidating low-level circulation center slightly to the east of the deepening convection.”
Nathan is moving southeast. The Joint Typhoon Warning center expects Nathan to strengthen to about 70 knots (80.5 mph/120.6 kph) in a couple of days before weakening again and turning back to the west toward Queensland.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….





















