Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.

Atmospheric carbon dioxide is lower at the weekend.
The climate-monitoring station on Mauna Loa volcano on Hawaii, 3,400 metres above sea level, could hardly be farther away from it all. Yet even here there is no escaping the weekly rhythm of modern life. The observatory records lower concentrations of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere at the weekend than during the week.
Because there is no known natural cause of such a seven-day cycle, Randall Cerveny of Arizona State Univer

The world`s oldest fossilised vomit, believed to have come from a large marine reptile that lived 160 million years ago, has been discovered in a clay quarry in Peterborough by the University of Greenwich`s Professor Peter Doyle and Dr Jason Wood of the Open University.
The vomit contains the remains of dozens of belemnites – squid-like shellfish that lived in abundance in the seas around what is now Britain. The belemnites were eaten in great numbers by ichthyosaurs, large marine reptiles (

For several days last week, the protective ozone layer over Europe thinned considerably. Scientists monitoring ozone coverage using a rapid mapping technique based on data from the GOME (Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment) instrument aboard ESA`s ERS-2 satellite detected finger-like ozone thinning over Europe.
“From 28-30 January, we observed a pronounced `streamer event`,” explains DLR`s Thilo Erbertseder, “where streamers of tropical air pushing up from the equatorial regions spread over s

30 years of slowing Pacific circulation may have changed climate
A recent slowing in the circulation of Pacific Ocean waters could have raised Pacific sea surface temperatures. It may even mean that less carbon has reached the atmosphere from the ocean surface over the past two decades.
Across the Pacific, water circulates in two giant loops in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. It flows from the subtropics to the tropics about at a depth of 100-400 metres, rises to the
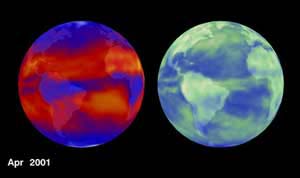
Climate prediction just got trickier, according to two new studies appearing in the current issue of the journal Science. Analysis of more than two decades of satellite data shows that more sunlight entered the tropics and more heat escaped to space in the 1990s than a decade earlier. Moreover, current climate models fail to account for the new findings, suggesting that they may contain more uncertainty than previously thought.
For the earth’s climate to remain unchanged, the planet’s ener

Researchers from the University of Amsterdam have demonstrated that the climate in South Mexico changed following the collapse of the Maya empire. From preserved pollen grains the paleoecologists could deduce that the climate quickly became dryer.
The climate becoming dryer, explains the decrease in the population following the collapse of the Maya empire. The climate researchers have therefore helped to solve an archaeological mystery.
With the help of pollen grains, the paleoeco