Discovery of a new function of the cerebellum
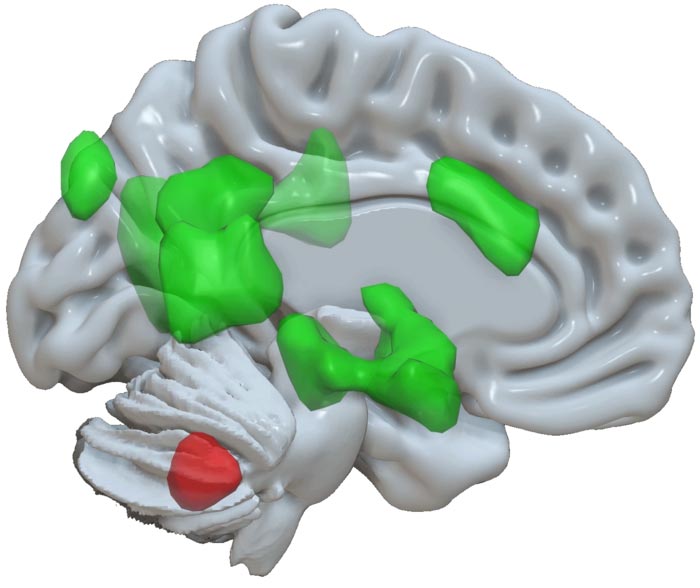
The cerebellum (activation in red) communicates with various areas of the cerebrum (activations in green) to enhance storage of emotional information.
Credit: MCN, University of Basel
The cerebellum is known primarily for regulation of movement. Researchers at the University of Basel have now discovered that the cerebellum also plays an important role in remembering emotional experiences. The study appears in the journal PNAS.
Both positive and negative emotional experiences are stored particularly well in memory. This phenomenon is important to our survival, since we need to remember dangerous situations in order to avoid them in the future. Previous studies have shown that a brain structure called the amygdala, which is important in the processing of emotions, plays a central role in this phenomenon. Emotions activate the amygdala, which in turn facilitates the storage of information in various areas of the cerebrum.
The current research, led by Professor Dominique de Quervain and Professor Andreas Papassotiropoulos at the University of Basel, investigates the role of the cerebellum in storing emotional experiences. In a large-scale study, the researchers showed 1,418 participants emotional and neutral images and recorded the subjects’ brain activity using magnetic resonance imaging.
In a memory test conducted later, the positive and negative images were remembered by the participants much better than the neutral images. The improved storage of emotional images was linked with an increase in brain activity in the areas of the cerebrum already known to play a part. However, the team also identified increased activity in the cerebellum.
The cerebellum in communication with the cerebrum
The researchers were also able to demonstrate that the cerebellum shows stronger communication with various areas of the cerebrum during the process of enhanced storage of the emotional images. It receives information from the cingulate gyrus – a region of the brain that is important in the perception and evaluation of feelings. Furthermore, the cerebellum sends out signals to various regions of the brain, including the amygdala and hippocampus. The latter plays a central role in memory storage.
“These results indicate that the cerebellum is an integral component of a network that is responsible for the improved storage of emotional information,” says de Quervain. Although an improved memory for emotional events is a crucial mechanism for survival, it does have its downsides: in the case of very negative experiences, it can lead to recurring anxiety. This means that the findings, which have now been released, may also be relevant in understanding psychiatric conditions such as post-traumatic stress disorder.
Basel research on emotions and memory
The current study forms part of a large-scale research project conducted by the Research Platform Molecular and Cognitive Neurosciences (MCN) at the University of Basel and the University Psychiatric Clinics (UPK) Basel. The aim of this project is to gain a better understanding of emotional and cognitive processes and to transfer results from basic research to clinical projects.
Journal: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2204900119
Article Title: Human cerebellum and corticocerebellar connections involved in emotional memory enhancement
Article Publication Date: 7-Oct-2022
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles

Hubble Views the Dawn of a Sun-like Star
Looking like a glittering cosmic geode, a trio of dazzling stars blaze from the hollowed-out cavity of a reflection nebula in this new image from NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The…

Engineering a new color palette for single-molecule imaging
A new paper published in Nature Nanotechnology outlines a way to create dozens of new “colors” to multiplex single-molecule measurements. Researchers often study biomolecules such as proteins or amino acids…

Using solar energy to generate heat at high temperatures
The production of cement, metals and many chemical commodities requires extremely high temperatures of over a thousand degrees Celsius. At present, this heat is usually obtained by combusting fossil fuels:…





















