NASA's SDO Spots a Summer Solar Flare
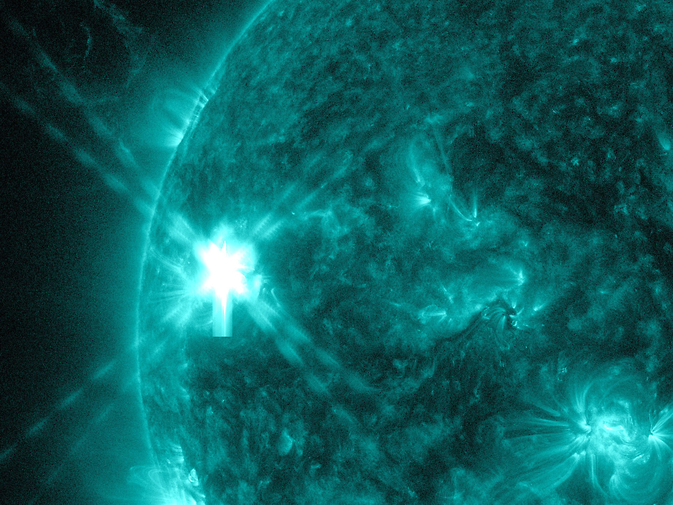
A mid-level flare erupted on the left side of the sun on July 8, 2014. This image from NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory highlights light of 171 Angstroms, which highlights the hot temperature of solar material in a flare and which is typically colorized in teal. Image Credit: NASA/SDO
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however — when intense enough — they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
This flare is classified as an M6.5-class flare.
Updates will be provided as they are available on the flare and whether there was an associated coronal mass ejection or CME, another solar phenomenon that can send solar particles into space and affect electronic systems in satellites and on Earth.
What is a solar flare? What is a CME?
For answers to these and other space weather questions, please visit the Spaceweather Frequently Asked Questions page.
Related Link
Karen C. Fox
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Trotting robots reveal emergence of animal gait transitions
A four-legged robot trained with machine learning by EPFL researchers has learned to avoid falls by spontaneously switching between walking, trotting, and pronking – a milestone for roboticists as well…

Innovation promises to prevent power pole-top fires
Engineers in Australia have found a new way to make power-pole insulators resistant to fire and electrical sparking, promising to prevent dangerous pole-top fires and reduce blackouts. Pole-top fires pose…

Possible alternative to antibiotics produced by bacteria
Antibacterial substance from staphylococci discovered with new mechanism of action against natural competitors. Many bacteria produce substances to gain an advantage over competitors in their highly competitive natural environment. Researchers…





















