Wrangling Flow to Quiet Cars and Aircraft
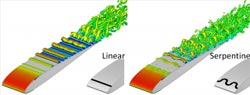
M. Riherd, APRG<br><br>Comparison of turbulent flow structures over an airfoil when a pulsed linear (left) and a serpentine (right) plasma actuator are used to control the flow.<br>
Plasmas are a soup of charged particles in an electric field, and are normally found in stars and lightning bolts. With the use of high voltage equipment, very small plasmas can be used to manipulate fluid flows.
In recent years, the development of devices known as plasma actuators has advanced the promise of controlling flows in new ways that increase lift, reduce drag and improve aerodynamic efficiencies — advances that may lead to safer, more efficient and more quiet land and air vehicles in the near future.
Unlike other flow control devices, plasma actuator geometries can be easily modified. Enter the serpentine shape, courtesy of the Applied Physics Research Group (APRG), a University of Florida research team in Gainesville that has been developing this and other types of novel plasma actuators for several years. The serpentine's sinuous, ribbon-like curves appear to impart greater levels of versatility than traditional geometries used in plasma flow control devices, according to Mark Riherd, a doctoral candidate working under Subrata Roy, the founding director of APRG.
“Our serpentine device will have applications in reducing drag-related fuel costs for an automobile or an aircraft, minimizing the noise generated when flying over populated areas, mixing air-fuel mixtures for lean combustion, and enhancing heat transfer by generating local turbulence,” Riherd said.
In a report appearing in the Journal of Applied Physics, which is produced by AIP Publishing, the team validated the complex, three-dimensional flow structures induced by their serpentine plasma actuators by comparing numerical results with recent physical experiments in non-moving air. They then simulated the effects of the actuators in a non-turbulent boundary layer and over a small aircraft wing. Further tests are needed, but early results suggest serpentine flow wrangling may improve transportation efficiencies.
“This may result in significant weight and fuel savings for future aircraft and automobiles, improving energy efficiency all around,” Riherd said.
The article, “On Using Serpentine Geometry Plasma Actuators for Flow Control” by Mark Riherd and Subrata Roy appears in the Journal of Applied Physics. See: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4818622
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
The Journal of Applied Physics, produced by AIP Publishing, is an influential international journal featuring significant new experimental and theoretical results of applied physics research. See: http://jap.aip.org
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.aip.orgAll latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















