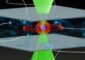
Dying Sun-like stars leave whirlpools in their wake

Dr Wareing and his colleagues used the COBRA supercomputer to simulate in three-dimensions the movement of a dying star through surrounding interstellar gas. At the end of their life, Sun-sized stars lose their grip on their outer layers and as much as half of their mass drifts off into space.
The computer simulation modelled the collision between material given off by the star and the interstellar gas. It showed that a shockwave forms ahead of the dying star and giant eddies and whirlpools develop in the tail of material behind the star, similar to those seen in the wake of boats on open water. The group have now backed up these predictions with observations of the planetary nebula Sharpless 2-188 taken as part of the IPHAS (Isaac Newton Telescope Photometric H alpha Survey of the Northern Galactic Plane).
The central star of Sharpless 2-188 is 850 light years away and it is travelling at 125 kilometres per second across the sky. Observations show a strong brightening in the direction in which the star is moving and faint material stretching away in the opposite direction. Dr Wareing believes that the bright structures in the arc observed ahead of Sharpless 2-188 are the bowshock instabilities revealed in his simulations, which will form whirlpools as they spiral past the star downstream to the tail.
“These vortices can improve the mixing of the stellar material back into interstellar space, benefiting the next cycle of star formation. The turbulent whirlpools have an inherent spin, or angular momentum, which is an essential ingredient for the formation of the next generation of stars.” said Dr Wareing who developed the computer model during his PhD and is now using it to understand the fate of our Sun.
Dying stars eject both gas and dust into space. The dust will coalesce into planets around later generations of stars. The gas contains carbon, necessary for life and produced inside stars. How the carbon, other gas and dust are ejected from the dying star is not well understood. The whirlpools in space can play an important role in mixing these essential ingredients into the interstellar gas from which further stars and planets will form.
IPHAS
IPHAS is a major survey of the Northern Galactic Plane being carried out with the 2.5-metre Isaac Newton Telescope (INT) in La Palma. The IPHAS survey began taking data with the INT Wide Field Camera in 2003 with the goal of imaging the entire northern galactic plane in the latitude range -5°
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Physics and Astronomy
This area deals with the fundamental laws and building blocks of nature and how they interact, the properties and the behavior of matter, and research into space and time and their structures.
innovations-report provides in-depth reports and articles on subjects such as astrophysics, laser technologies, nuclear, quantum, particle and solid-state physics, nanotechnologies, planetary research and findings (Mars, Venus) and developments related to the Hubble Telescope.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…