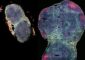
Underestimation of Frog Numbers Causes Concern

In a paper published in the online, open-access journal PLoS ONE, a team of experts, including researchers from the University of Canterbury, says the number of species has been strongly underestimated and they are calling for action.
The researchers from France and New Zealand collected and collated more than 500 DNA sequences, including 60 previously recognised species, occurring in the Guiana Shield, which harbours the largest continuous tract of virgin tropical rainforest.
This region of Amazonia comprises French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, eastern Venezuela and northern Brazil.
PhD researcher Antoine Fouquet says the samples revealed an astonishing level of cryptic diversity, with the number of species identified potentially two-fold greater than previously thought.
Antoine says such underestimation of amphibian diversity has broad implications for the management of biodiversity, and particularly that of many Neotropical amphibians which are considered highly threatened.
He says frogs are the “canaries in the coal mine” and their current decline is regarded as an indicator of the environmental crisis.
“Given the unique evolutionary history of the Guiana Shield region, and its nearly pristine condition, it is critical that there is greater understanding of its frog species.”
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.plosone.org/doi/pone.0001109All latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
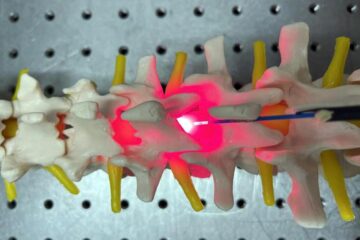
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….