DNA clues to inform conservation in Africa

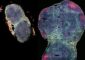
Researchers in the School of Biosciences analysed the African bushbuck, a common species which lives in most sub-Saharan habitat types to test whether DNA similarity between populations living in different habitats can reveal the similarity of those ecoregions now and in the past.
The study, one of the first of its kind, identified 28 key regions for bushbucks. By understanding the genetic similarity of populations inhabiting different habitats researchers found they can potentially trace which ecoregions are most similar and establish which are the most unique in evolutionary history.
Professor Mike Bruford, School of Biosciences, co-author of the study, said: “The conservation of habitat or ecoregion biodiversity is one of our greatest challenges. This new approach will allow conservationists in Africa to focus their efforts on the most biodiverse and more unique habitats which harbour the most genetically distinct populations.”
The researchers suggest the study provides a framework for the incorporation of genetic and biogeographic information into a more widely applicable model for pan-African conservation and, potentially, for the conservation of other global regions.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.cardiff.ac.ukAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
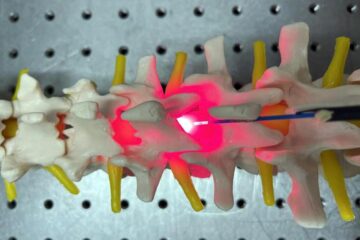
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….