The immunology of Helicobacter pylori infection

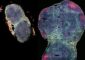
H. pylori is a Gram-negative, spiral bacterium that colonizes the gastric mucosa of at least 50% of the world's population and plays a causative role in the development of chronic gastritis as well as in gastric and duodenal ulcers. The overall prevalence of H. pylori infection is strongly correlated with socioeconomic conditions, with a prevalence of more than 80% in many developing countries.
H. pylori triggers vigorous humoral and cellular immune responses in both systemic and mucosal compartments. In spite of this response, the vast majority of infected hosts are unable to clear the infection, and it persists for decades, causing continuous gastric inflammation in virtually all infected persons.
Although Helicobacter is tolerated by a naïve host organism, preclinical studies have demonstrated that prophylactic or therapeutic vaccinations efficiently clear Helicobacter from the stomach. Mast cells and CD4+ T cells appear as key players. However, the mechanisms of action remain open. The understanding of these mechanisms leading to the Helicobacter persistence or the vaccine-induced eradication of Helicobacter in animal models will help to define optimal immunization strategies for future anti-Helicobacter vaccination clinical trials.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.karger.comAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
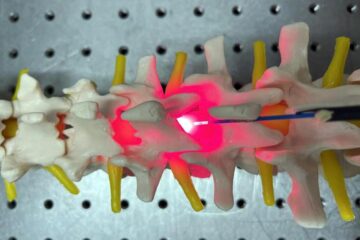
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….