Breakthrough in West Nile disease

West Nile virus (WNV) is a serious infection spreading across the world.
Spread by mosquitoes, it can cause high fever, encephalitis, stupor, disorientation, coma, tremors, convulsions, muscle weakness, loss of vision, numbness, paralysis and death. There is no vaccine and no cure.
Now, there is a chance that a team of researchers have identified a promising drug target.
In the latest issue of the Biochemical Journal, Alex Strongin of The Burnam Institute, La Jolla, and co-workers report that the NS3 protease from West Nile virus unexpectedly cleaves certain substrates at pairs of basic residues, a specificity that resembles that of the furin-like PCs (proprotein convertases).
This suggests that furin/PC inhibitors containing poly(D-arginine) could be used as inhibitors of NS3, and that anthrax toxin protective antigen and myelin basic protein are potential NS3 substrates.
The hope is that the isolation of small-molecule inhibitors to WNV NS3 could at least lower the viral burden, and could lead to a clinically-effective drug.
Media Contact
More Information:
http://www.biochemj.org/bj/393/0503/3930503.pdfAll latest news from the category: Life Sciences and Chemistry
Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
Newest articles
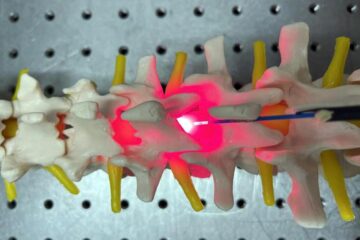
Red light therapy for repairing spinal cord injury passes milestone
Patients with spinal cord injury (SCI) could benefit from a future treatment to repair nerve connections using red and near-infrared light. The method, invented by scientists at the University of…

Insect research is revolutionized by technology
New technologies can revolutionise insect research and environmental monitoring. By using DNA, images, sounds and flight patterns analysed by AI, it’s possible to gain new insights into the world of…

X-ray satellite XMM-newton sees ‘space clover’ in a new light
Astronomers have discovered enormous circular radio features of unknown origin around some galaxies. Now, new observations of one dubbed the Cloverleaf suggest it was created by clashing groups of galaxies….