NASA Spotted Hot Towers in Ileana That Indicated its Increase to Hurricane Status
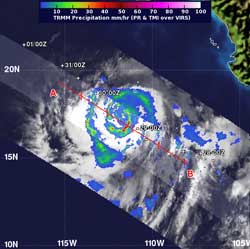
NASA's TRMM satellite captured a view of Ileana's rainfall rates on Aug. 29 at 2:17 a.m. EDT. The purple areas indicated the heaviest rainfall rates, near 70 mm (2.7 inches) per hour. Some hot towering clouds around the center of circulation (also in purple) were higher than 9.3 miles (15 km). Credit: NASA/SSAI, Hal Pierce<br>
NASA research indicates that whenever a hot tower is spotted, a tropical cyclone will likely intensify. Less than 14 hours after the TRMM satellite captured an image of Ileana's rainfall and cloud heights, Ileana strengthened into a hurricane on Aug. 29.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission (TRMM) satellite captured a view of Ileana's rainfall rates on Aug. 29 at 2:17 a.m. EDT and saw the heaviest rainfall rates, near 50 mm (2.0 inches) per hour in a band of thunderstorms southeast of the center of circulation. TRMM identified some hot towering clouds around the center of circulation that were higher than 9.3 miles (15 km).
On Aug. 30, satellite data showed a ragged double eyewall in the center of circulation. On Aug. 30 at 11 a.m. EDT, Hurricane Ileana's maximum sustained winds had increased to near 80 mph (130 kmh). Hurricane force winds extend outward up to 25 miles (35 km) from the center, which makes Ileana's hurricane-force wind area about 15 miles larger than Hurricane Kirk's in the Atlantic Ocean today. Ileana's tropical storm force winds extend outward up to 90 miles (150 km).The National Hurricane Center expects that Ileana won't strengthen much more before weakening on Aug. 31.
Ileana's center was about 305 miles (495 km) southwest of the southern tip of Baja California, Mexico, near latitude 20.2 north and longitude 113.7 west. Ileana is moving toward the northwest near 8 mph (13 kmh) and into cooler waters that will sap her strength.
The National Hurricane Center expects Ileana to weaken to a remnant low pressure area over the weekend of Sept. 1-2, while drifting west, and away from land.
Text credit: Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Sea slugs inspire highly stretchable biomedical sensor
USC Viterbi School of Engineering researcher Hangbo Zhao presents findings on highly stretchable and customizable microneedles for application in fields including neuroscience, tissue engineering, and wearable bioelectronics. The revolution in…

Twisting and binding matter waves with photons in a cavity
Precisely measuring the energy states of individual atoms has been a historical challenge for physicists due to atomic recoil. When an atom interacts with a photon, the atom “recoils” in…

Nanotubes, nanoparticles, and antibodies detect tiny amounts of fentanyl
New sensor is six orders of magnitude more sensitive than the next best thing. A research team at Pitt led by Alexander Star, a chemistry professor in the Kenneth P. Dietrich…





















