NASA-NOAA satellite sees the end of Tropical Cyclone Ikola
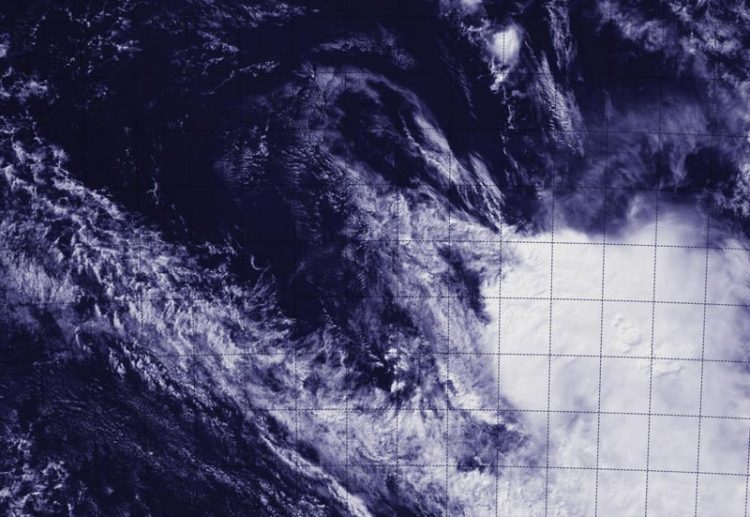
This image of Ikola was taken on April 8 from NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite and showed strong wind shear pushed the clouds far southeast of the center. That wind shear also elongated the storm. Credit: NRL/NASA/NOAA
When Suomi NPP flew over Tropical Cyclone Ikola at 07:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EDT), the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard captured a visible image of the storm.
VIIRS is a scanning radiometer that collects visible and infrared imagery and “radiometric” measurements. Basically it means that VIIRS data is used to measure cloud and aerosol properties, ocean color, sea and land surface temperature, ice motion and temperature, fires, and Earth's albedo (reflected light).
The VIIRS image showed that the storm had basically unraveled and the bulk of clouds associated with it were pushed about 150 nautical miles (172.6 miles/277.8 km) southeast of the center. The thunderstorms were pushed by strong northwesterly vertical wind shear blowing between 40 and 50 knots. That wind shear also elongated the storm.
At 09:00 UTC (5 a.m. EDT), Tropical Cyclone Ikola's maximum sustained winds had dropped to 35 knots (40 mph/65 kph). It was centered near 21.2 south latitude and 98.6 east longitude, about 1,017 nautical miles (1,170 miles/1,883 km) west of Learmonth, Western Australia. Ikola was moving to the east at 12 knots (13.8 mph/22.2 kph), but fading fast.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast called for the strong northwesterly vertical wind shear to continue to deteriorate the system and lead to its dissipation later today.
###
The Suomi NPP mission is a bridge between NOAA and NASA legacy Earth observing missions and NOAA's next-generation Joint Polar Satellite System, or JPSS.
Media Contact
All latest news from the category: Earth Sciences
Earth Sciences (also referred to as Geosciences), which deals with basic issues surrounding our planet, plays a vital role in the area of energy and raw materials supply.
Earth Sciences comprises subjects such as geology, geography, geological informatics, paleontology, mineralogy, petrography, crystallography, geophysics, geodesy, glaciology, cartography, photogrammetry, meteorology and seismology, early-warning systems, earthquake research and polar research.
Newest articles

Why getting in touch with our ‘gerbil brain’ could help machines listen better
Macquarie University researchers have debunked a 75-year-old theory about how humans determine where sounds are coming from, and it could unlock the secret to creating a next generation of more…

Attosecond core-level spectroscopy reveals real-time molecular dynamics
Chemical reactions are complex mechanisms. Many different dynamical processes are involved, affecting both the electrons and the nucleus of the present atoms. Very often the strongly coupled electron and nuclear…

Free-forming organelles help plants adapt to climate change
Scientists uncover how plants “see” shades of light, temperature. Plants’ ability to sense light and temperature, and their ability to adapt to climate change, hinges on free-forming structures in their…





















