Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.

Chemical force microscopy chooses materials for lightweight nanotube-based composites
Nanocomposites for space
A microscopy technique originally developed to image the molecular-scale topography of surfaces is now helping engineers choose the right materials for a new generation of lightweight high-strength composites based on carbon nanotubes.
Light, conductive and nearly as strong as steel, carbon nanotubes are being combined with lightweight polymers to produce composite materials with properties attractive for use on future space vehicles. But choosing th
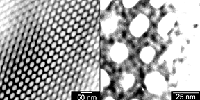
Porous ceramic can sort proteins magnetically
In recent years chemists and materials scientists have enthusiastically searched for ways to make materials with nanoscale pores — channels comparable in size to organic molecules — that could be used, among other things, to separate proteins by size. Recently Cornell University researchers developed a method to “self-assemble” such structures by using organic polymers to guide the formation of ceramic structures.
Now they have advanced another step by incorporating tiny magnetic particle

Making plastic smarter with protein
How do you improve on plastic, a modern material that has already changed the way we do everything from design medical devices to build cars? Embed it with specialized proteins called enzymes, says Shekhar Garde, assistant professor of chemical engineering at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute.
“Such protein-enhanced plastics might someday be able to act as ultra-hygienic surfaces or sensors to detect the presence of various chemicals,” says Garde. These types of materials could have a wide
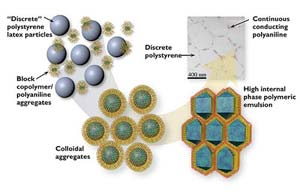
Mayonnaise as Model for Solid Plastics
Intriguing Structural Strategy Aims at Making Designer Plastics Affordable
The future was supposed to be “plastics,” according to advice given in a 1960s movie The Graduate. Many a company thought that future meant the gradual ascendancy of “designer” or specialty plastics, but almost 40 years later the market is still dominated by plastics that can be manufactured cheaply in bulk.
Six researchers from the University of California at Santa Barbara (UCSB) and one at Helsinki U

New Measurements Show Silicon Nanospheres Rank Among Hardest Known Materials
University of Minnesota researchers have made the first-ever hardness measurements on individual silicon nanospheres and shown that the nanospheres’ hardness falls between the conventional hardness of sapphire and diamond, which are among the hardest known materials. Being able to measure such nanoparticle properties may eventually help scientists design low-cost superhard materials from these nanoscale building blocks.
Up to four times harder than typical silicon-a principal ingredient o

Concrete less sensitive for cracks than previously thought
Reinforced high-strength concrete can crack due to stresses that develop during the hardening process. However, this has been found to be surprisingly less quick than previously thought. Due to Dutch research, extra steps during the hardening process can be omitted. This will result in cheaper concrete.
Maya Sule from Delft University of Technology tested specimens of high strength concrete (concrete with little water) in a temperature stress testing machine (TSTM). Such tests indicate the