Materials Sciences
Materials management deals with the research, development, manufacturing and processing of raw and industrial materials. Key aspects here are biological and medical issues, which play an increasingly important role in this field.
innovations-report offers in-depth articles related to the development and application of materials and the structure and properties of new materials.

New Type of Strong, Lightweight Metallic Material
An engineering professor at the University of California, San Diego has described in the March issue of JOM (the Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society) the unique properties of a new type of metallic laminate that can serve as armor and as a replacement for beryllium, a strong but toxic metal commonly used in demanding aerospace applications.
“The new material we developed is environmentally safe, and while its stiffness equals that of steel, it’s only half as

Researcher describes new type of strong, lightweight metallic material
A new type of laminate performed spectacularly in depth-of-penetration ballistics tests, but its greatest potential may derive from its ability to be tailored to meet specific engineering requirements
An engineering professor at the University of California, San Diego has described in the March issue of JOM (the Journal of the Minerals, Metals and Materials Society) the unique properties of a new type of metallic laminate that can serve as armor and as a replacement for berylliu

High-Fidelity Patterns Form Spontaneously When Solvent Evaporates
Resembling neatly stacked rows of driftwood abandoned by receding tides, particles left by a confined, evaporating droplet can create beautiful and complex patterns. The natural, pattern-forming process could find use in fields such as nanotechnology and optoelectronics.
“A lot of work in nanotechnology has been directed toward the bottom-up imposition of patterns onto materials,” said Steve Granick, a professor of materials science, chemistry and physics at the University of Ill

Next Research-TV broadcast: Friday 4 March
The next Research-TV broadcast will take place on Friday 04 March 09:15 – 09:30 GMT and will feature one topical technology story.
Research-TV produces VNRs tailor made for TV news, radio, online and written coverage. Each story highlights groundbreaking research and/or new discoveries.
——————-
EU Research Infrastructures
Materials Science and Nanotechnology – The Big Picture
The study of materials science starts small – in the nanometre

Ames Laboratory research may lead to hotter-running engines
Researchers at the U. S. Department of Energy’s Ames Laboratory and Iowa State University have developed a new bond coat for thermal barrier coatings, or TBCs, that may allow gas turbine engines in aircraft and other power-generating technologies to better withstand severe, high-temperature environments. The basic research effort could provide a TBC system with significantly improved reliability and durability of turbine blades, thus enabling higher operating efficiencies and extending engine l
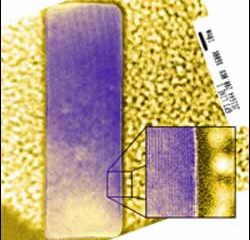
NIST unveils atom-based standards
Device features on computer chips as small as 40 nanometers (nm) wide–less than one-thousandth the width of a human hair–can now be measured reliably thanks to new test structures developed by a team of physicists, engineers, and statisticians at the Commerce Department’s National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), SEMATECH, and other collaborators. The test structures are replicated on reference materials that will allow better calibration of tools that monitor the manufacturing of