Articles and reports from the Life Sciences and chemistry area deal with applied and basic research into modern biology, chemistry and human medicine.
Valuable information can be found on a range of life sciences fields including bacteriology, biochemistry, bionics, bioinformatics, biophysics, biotechnology, genetics, geobotany, human biology, marine biology, microbiology, molecular biology, cellular biology, zoology, bioinorganic chemistry, microchemistry and environmental chemistry.
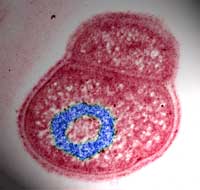
The secret to its strength is a ring, Weizmann Institute researchers report in Science
Weizmann Institute scientists have found what makes the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans the most radiation-resistant organism in the world: The microbe’s DNA is packed tightly into a ring. The findings, published in the January 10 issue of Science, solve a mystery that has long engaged the scientific community.
The red bacterium can withstand 1.5 million rads – a thousand times more tha

A University at Buffalo chemist has developed a new, high-throughput method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) data that not only has the distinction of potentially performing orders of magnitude faster than conventional methods, but does so more cheaply and with greater precision.
The new method, described in the current online issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society, has the potential to increase greatly the use of high-throughput NMR to determine protein structu

University of Georgia researchers studying rice genomes under a National Science Foundation Plant Genome Research Program award have identified the species’ first active DNA transposons, or “jumping genes.” The research is published in the Jan. 9 edition of the journal Nature. In collaboration with researchers from Cornell, Washington University and Japan, geneticist Susan Wessler also discovered the first active “miniature inverted-repeat transposable element,” or “MITE,” of a

In three separate studies, scientists at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill School of Medicine have shown that it is possible to correct defective molecular splicing pathways that would otherwise contribute to cancer, genetic diseases and possibly other disorders.
These corrections were accomplished by the insertion into the cell of antisense oligonucleotides, short strands of genetic material that target portions of RNA. RNA carries the DNA blueprint for cellular protein produ

Scientists from Johns Hopkins and the University of Wisconsin have discovered that a protein called Sir2, which is found in nearly all living cells, has a new function that might help explain how calorie restriction can increase lifespans for some animals, the scientists say. Their report appeared in the Dec. 20 issue of Science.
A number of laboratories have shown that restricting total calorie intake extends the lifespans of organisms ranging from yeast to laboratory animals. Others have

The biological clock – timekeeper for virtually every activity within living things, from sleep patterns to respiration – is a single protein, Purdue University researchers report.
The husband and wife team of D. James and Dorothy Morré has discovered this protein, which is responsible for setting the length of periods of activity and inactivity within cells. If the protein is altered, an organism’s body will experience “days” of different length – ranging from 22 to 42 hours in